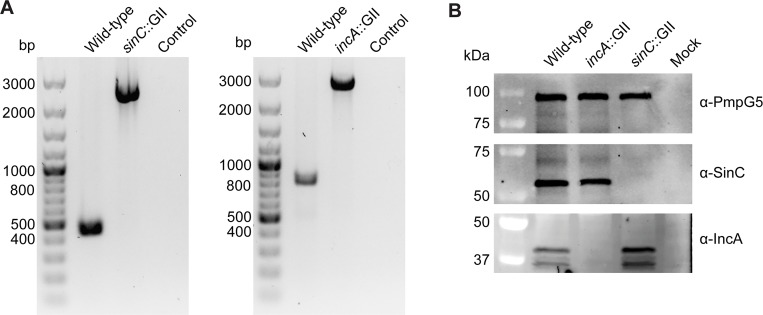
Fig 1. Insertional disruption of sinC and incA in the sinC::GII or incA::GII mutants of C. caviae GPIC.
(A) PCR-based verification of intron insertion at correct target sites. Primer sets binding to regions flanking either sinC (left) or incA (right) of C. caviae GPIC were used to confirm intron insertion at target sites in the respective mutant strains. The primers amplify fragments of 446 bp (sinC) and 822 bp (incA) in wild-type C. caviae GPIC in which the genes are intact, and fragments of 2335 bp (sinC) and 2711 bp (incA) in the mutants in which intron insertion occurred in the respective genes. “Control” refers to the PCR negative control in which only water was used as template. (B) Immunoblot analysis confirms absence of SinC and IncA protein in cells infected with sinC::GII or incA::GII mutants, respectively. Vero cells were infected with wild-type C. caviae GPIC, the sinC::GII or incA::GII mutant, or were mock infected. Protein samples were generated at 48 hpi. The representative blots shown were made with the same samples and same sample amounts loaded; IncA staining was conducted on a separate membrane. The calculated molecular masses of detected proteins are approximately 100.4 kDa (PmpG5), 49.4 kDa (SinC), and 38.8 kDa (IncA).