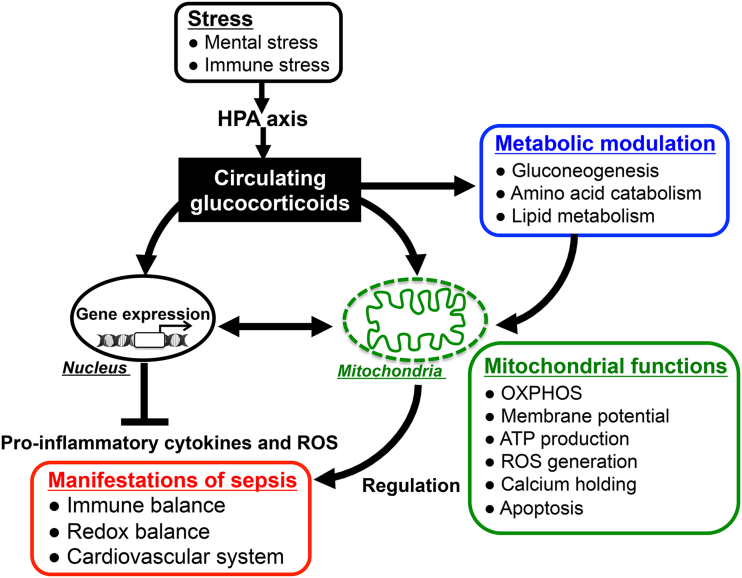
Figure 4.
Glucocorticoid actions for immunomodulation via nucleus- and mitochondria-dependent signaling pathways: Glucocorticoids have pleiotropic effects on energy metabolism (gluconeogenesis, amino acid catabolism, fatty acid metabolism), mitochondrial activity, and immune responses. The alteration of mitochondrial functions such as oxidative activity, ATP production, and apoptotic signaling in response to glucocorticoids plays important roles in modulating host immune responses and redox systems. Thus, appropriately stimulated HPA-axis followed by glucocorticoid release in response to endotoxin-induced immune stress might reduce the parameters of inflammatory response and improve the mortality in sepsis through both nucleus- and mitochondria-dependent signaling pathways.