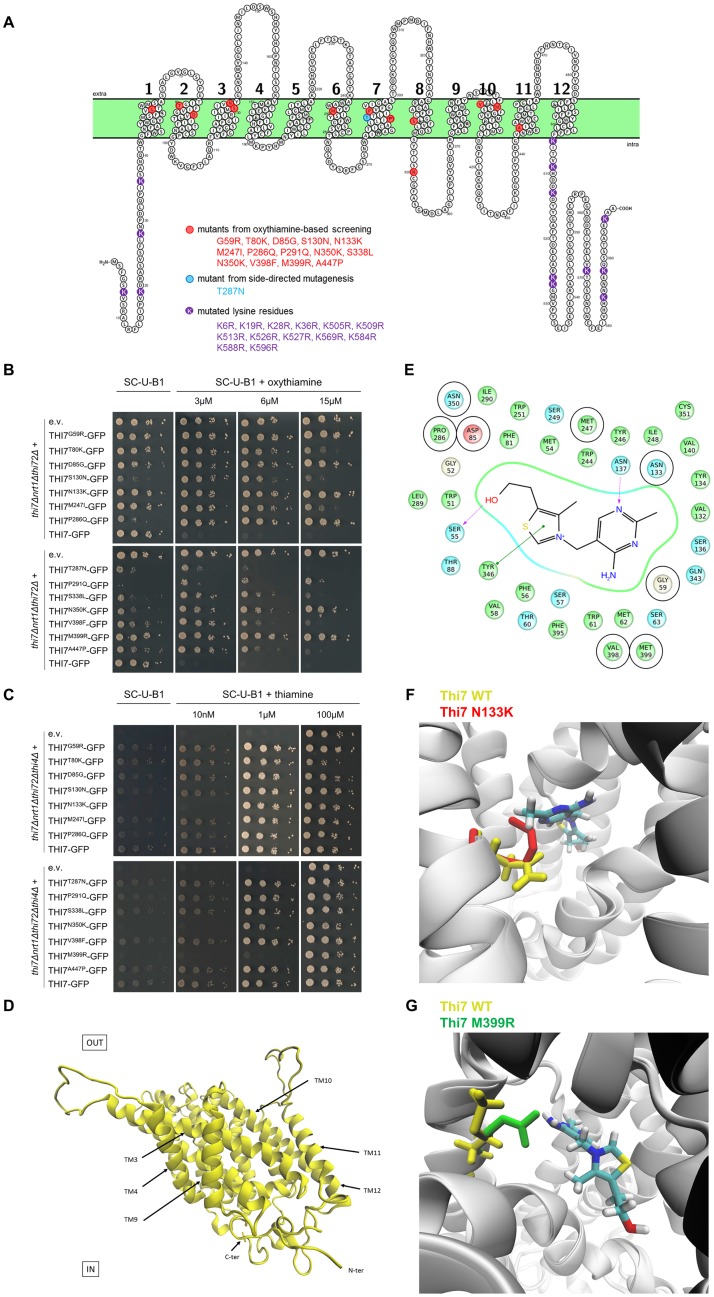
Fig 4. Selection of 14 single-point Thi7 mutants with reduced transport activity and structural modelling of Thi7.
(A) Scheme of Thi7 topology generated by Protter software [43], representing the 14 single-point Thi7 mutants isolated by oxythiamine-based screening (red) or by side-directed mutagenesis (blue). The lysine residues mutated to generate Thi7KR mutants are shown in purple. (B) Phenotypic growth test of thi7Δnrt1Δthi72Δ strain expressing single-point THI7-GFP mutants, WT THI7-GFP, or an e.v. on thiamine-free selective medium (SC-U-B1) supplemented or not with oxythiamine (final concentrations; 3, 6, and 15 μM). Representative of 5 experiments. (C) Phenotypic growth test of thi7Δnrt1Δthi72Δthi4Δ strain expressing single-point THI7-GFP mutants, WT THI7-GFP, or an e.v. on thiamine-free selective medium (SC-U-B1) or supplemented with thiamine (final concentrations; 10 nM, 1 μM, and 100 μM). Representative of 4 experiments. (D) A 3D model of Thi7 in an occluded state. (E) Proposed thiamine binding site in Thi7. Residues predicted to be at a distance equal to or less than 6 Å from the thiamine molecule are shown. Docking experiments predict that thiamine is stabilized by two hydrogen bridges with S55 and N137 (in purple) and one π-π interaction with Y346 (in green). Eight Thi7 mutants obtained in the oxythiamine-based screening result from mutation of specific residues surrounding the binding site (encircled in black: G59, D85, N133, M247, P286, N350, V398, M399). (F) Superimposition of the 3D model of WT Thi7 (residue N133 in yellow) in a thiamine-bound occluded state with the 3D model of Thi7N133K (residue K133 in red) in an occluded state displays how the N133K mutation could affect the binding site and the stabilization of thiamine. (G) Superimposition of the 3D model of WT Thi7 (residue M399 in yellow) in a thiamine-bound occluded state with the 3D model of Thi7M399R (residue R399 in green) in an occluded state displays how the M399R mutation could disturb the binding site and stabilization of thiamine. 3D, three-dimensional; C-ter, C terminus; e.v., empty vector; GFP, green fluorescent protein; KR, lysine-to-arginine; N-ter, N terminus; TM, transmembrane span; WT, wild type.