Figure 3.
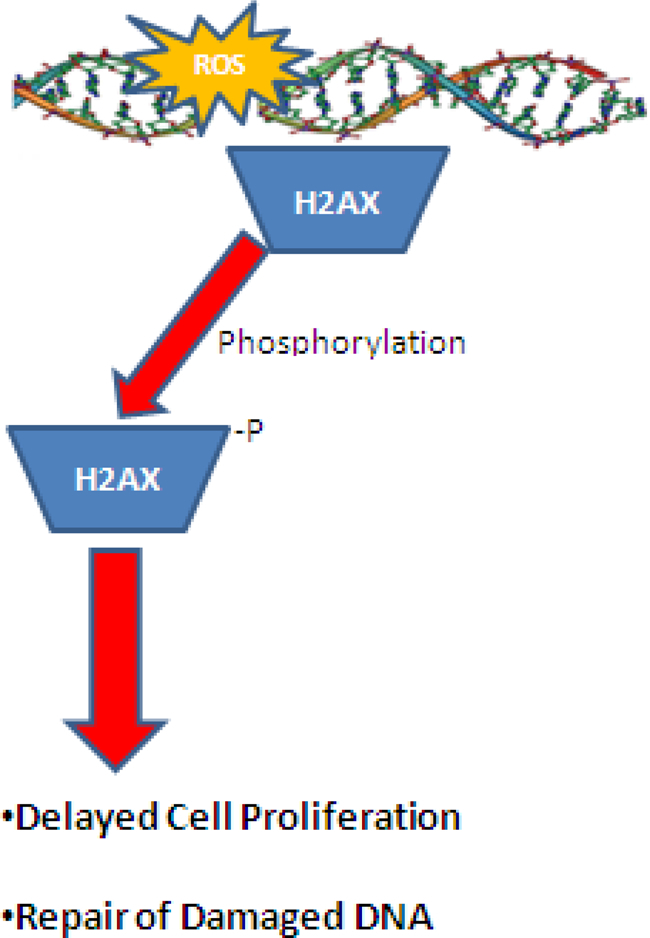
Phosphorylation of H2AX at Serine 139 following ROS damage to DNA. Under mild-to-moderate oxidative damage, phosphorylation of H2AX can lead to temporary cessation of cellular function and DNA repair. However, under extreme conditions, hyperphosphorylation of H2AX can lead to cell death via an apoptotic mechanism.
