Figure 4.
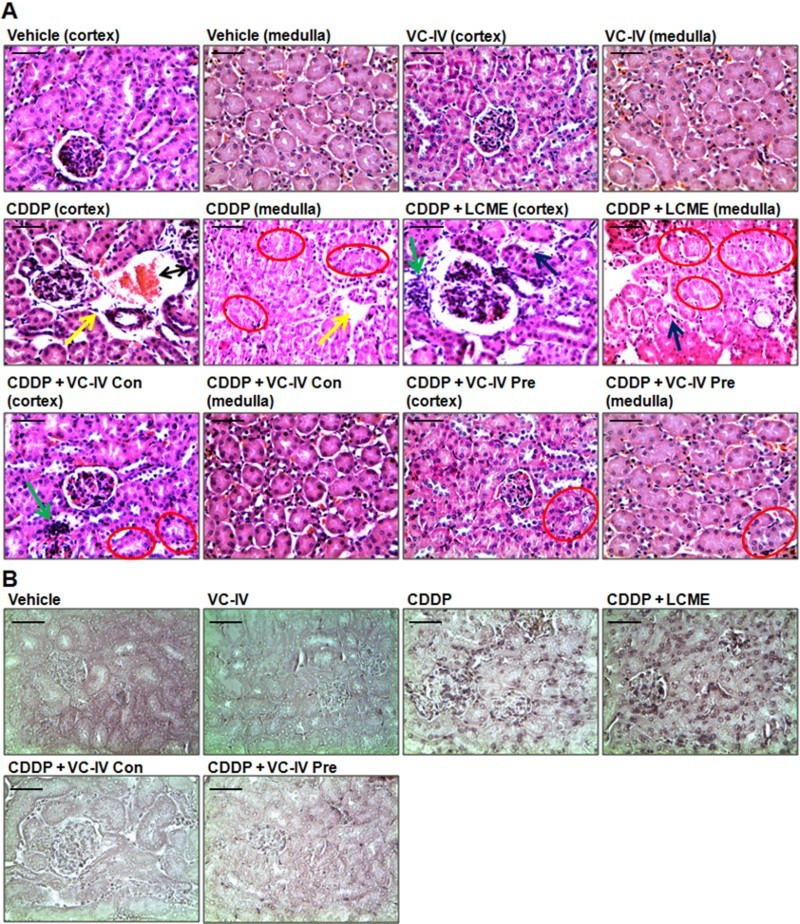
VC-IV reduced CDDP-induced renal damage in mice. (a) Photomicrographs of kidney sections of mice stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H and E). Normal histology with renal corpuscle, proximal, and distal convoluted tubules was observed in vehicle-treated and only VC-IV-treated group. Large area of interstitial hemorrhage (black color double headed arrow), atrophy (yellow color arrow) and loss of brush border (red color oval) were found in CDDP-treated group. Loss of brush border (red color oval), tubular dilatation (blue color arrow), and leukocyte infiltration (green color arrow) were found in CDDP + LCME-treated group. CDDP + VC-IV concomitant-treatment group showed moderate loss of brush border (red color oval) and mild leukocyte infiltration (green color border). Quite normal histology was observed in CDDP + VC-IV pre-treatment group except mild loss of brush border. (b) Photomicrographs of kidney sections of mice stained with TUNEL reagent (BCIP/NBT), × 400 magnification, scale bar = 50 μm. CDDP treatment resulted in apoptosis (TUNEL-labelled cells) around glomerulus and proximal convulated tubules. CDDP + LCME-treated group also showed apoptosis around glomerulus and proximal convulated tubules. Treatment with VC-IV in concomitant- and pre-treatment schedule showed null or minimal presence of apoptotic cells.
