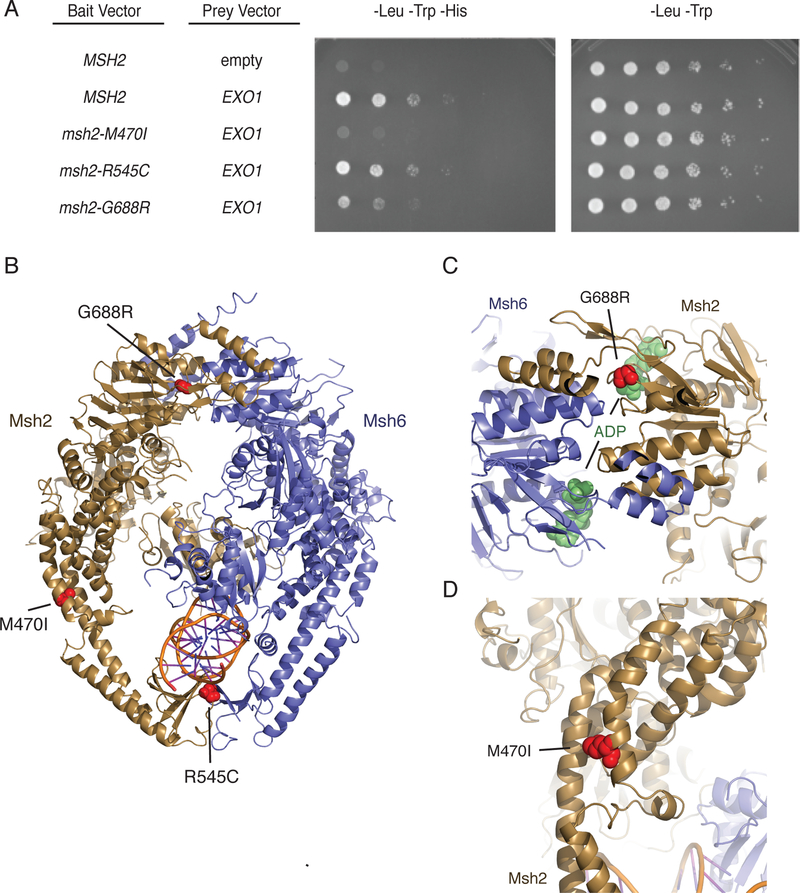
Figure 4. The msh2-M470I mutation disrupts the Msh2-Exo1 interaction.
A. Yeast two-hybrid analysis of wild-type EXO1 prey vectors with bait vectors carrying MSH2, msh2-M470I, msh2-R545C, and msh2-G688R reveal that Msh2-G688R has a partial Exo1 binding defect and that Msh2-M470I is defective for Exo1 binding. All experiments were independently repeated a minimum of 4 times. B. The positions of the S. cerevisiae M470I, R545C, and G688R amino acid substitutions were modelled onto the human Msh2-Msh6 structure (PDB id 2o8b, ref. 33). Msh2 is displayed in dark yellow ribbons, Msh6 is displayed in blue cartoon, and DNA is displayed as a cartoon. Positions of the amino acid substitutions are shown as red spheres. C. The G688R amino acid substitution affects a conserved glycine residue present in a loop adjacent to the Msh2 nucleotide-binding site that contains an ADP molecule (green spheres) in the human Msh2-Msh6 structure. D. The M470I amino acid substitution affects a conserved methionine present at a site where the helices in the helical arms that surround the DNA substrate pack against each other. The site is also N-terminal to a loop that interrupts these helices and might be a site of flexibility in the protein in the absence of DNA as revealed by DNA-free structures of Thermus aquaticus MutS60.