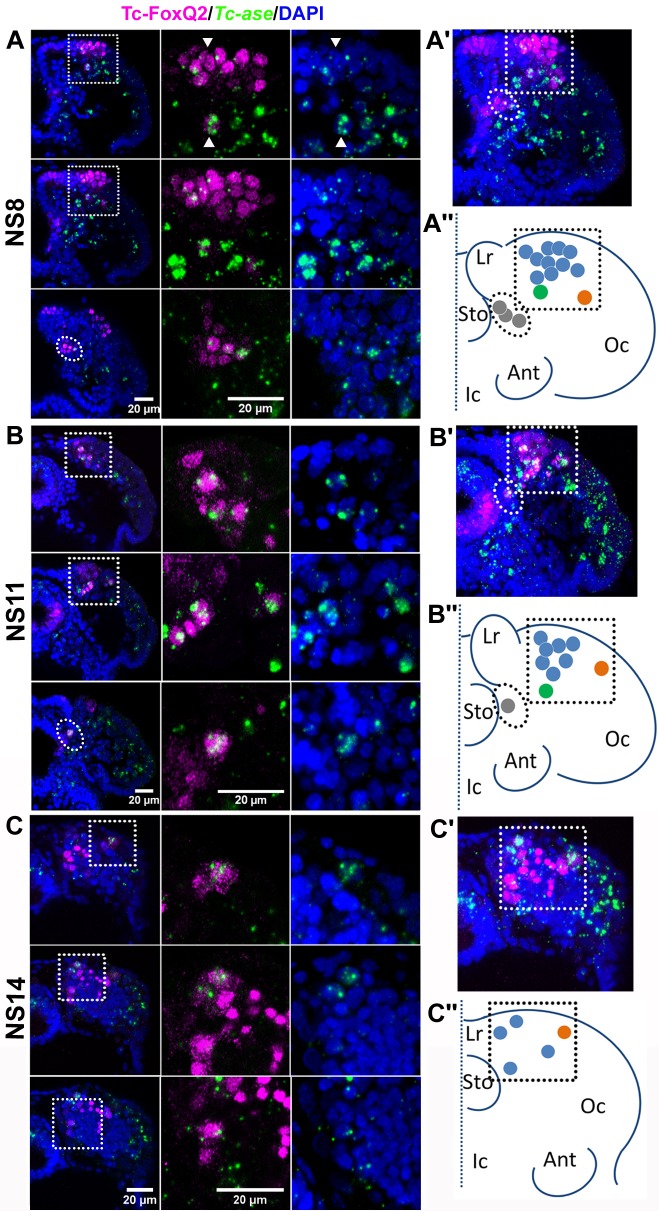
Figure 1. Tc-FoxQ2 positive neural progenitor cells.
Tc-FoxQ2 protein is visualized by immunohistochemistry at different stages (magenta) while neural progenitor cells (NPCs) are marked by intronic Tc-asense whole mount in situ hybridization (green). Nuclei are visualized by DAPI (blue). Optical sections of right halves of stained heads are shown in the left column while respective close-ups are shown in second and third column (see hatched areas in left column in (A, B and C). A projection of all optical sections is given in the right column (A’, B’ and C’). The schemes represent the outline of right halves of the head lobes of flattened embryos. The dotted line represents the midline. This depiction is comparable to the one previously used for Drosophila neuroblast maps (Urbach and Technau, 2003a) (A’’, B’’ and C’’). (A–A’’) At NS8 about 15 Tc-FoxQ2 positive NPCs are found (n = 6). By position, three groups are distinguished: A large anterior median group (blue in A’’) with one neuroblast slightly separated posteriorly (green in A’’), one single lateral NPC (orange in A’’) and a group located closely to the midline (gray in A’’). White arrowheads show two exemplary NPCs. (B–B’’) At NS11 about 10 Tc-FoxQ2 positive NPCs are observed (n = 6). (C–C’’) At NS14, the number has decreased to 5–7 cells (n = 6). The single lateral NPC remains distinguishable (orange in C’’). Lr: labrum; Sto: stomodeum; Oc: ocular region; Ant: antenna; Ic: Intercalary region.
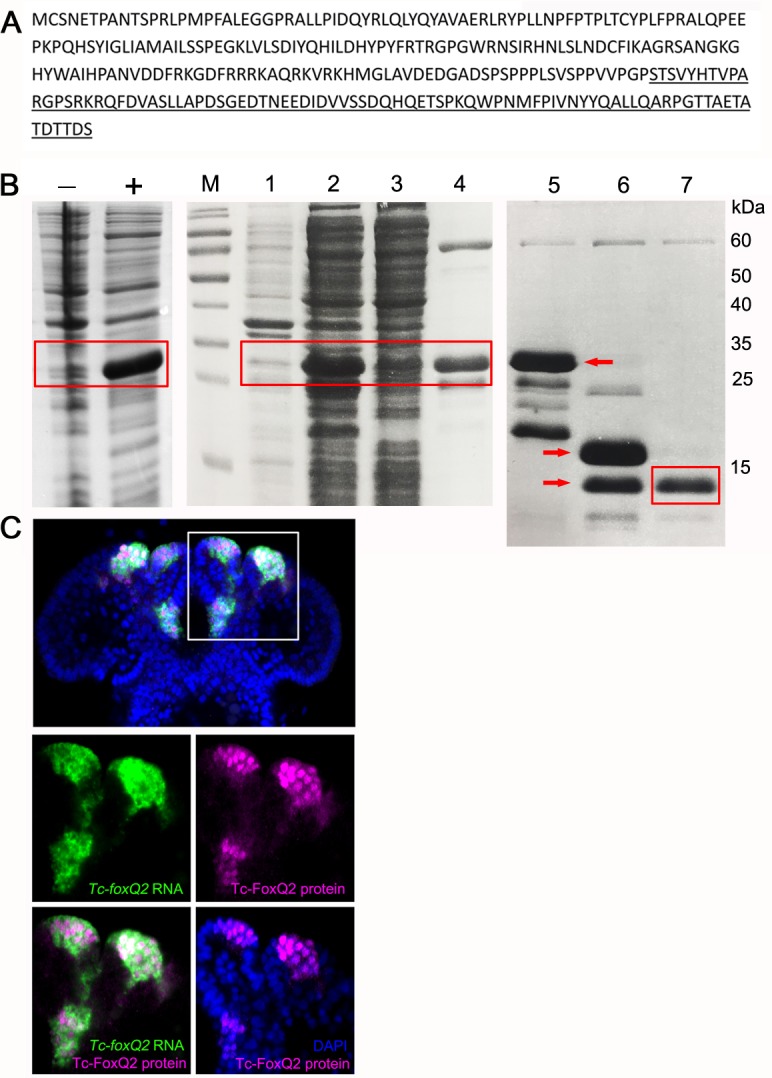
Figure 1—figure supplement 1. Generation of a Tc-FoxQ2 antibody.