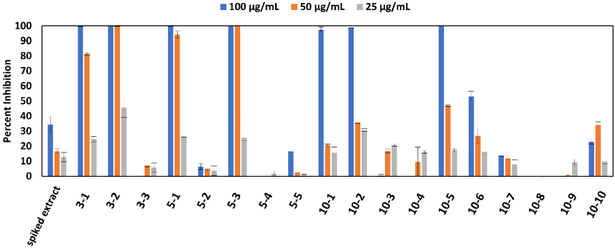
Figure 1.
Antimicrobial activity data of the A. keiskei root extract spiked with known antimicrobial compounds (spiked extract) and eighteen chromatographically separated pools from this original spiked extract. Pools labeled 3-1 through 3-3 represent samples resulting from chromatographic separation of the spiked A. keiskei root mixture into three pools, 5-1 through 5-5 represent samples from separation into five pools, and 10-1 through 10-10 represent samples from the ten-pool set. Growth inhibition of Staphylococcus aureus (SA1199)36 is displayed as percent growth inhibition normalized to the vehicle control (broth containing bacteria but no antimicrobial compound) using OD600 values. Data presented are the results of triplicate analyses ± SEM. Pure compounds berberine (1), magnolol (2), cryptotanshinone (3), and α-mangostin (4) served as positive controls and their minimum inhibitory concentrations (75, 6.25, 12.5, and 1.56 μg/mL, respectively), are consistent with previous reports. 9,37-39