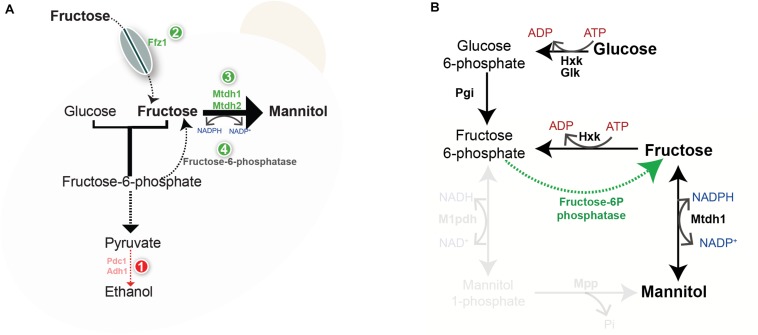
FIGURE 5.
Working model for the evolution of mannitol metabolism. (A) Lack of or inefficient alcoholic fermentation (1) causes redox constraints that can be partly alleviated by oxidized cofactor recycling by the mannitol dehydrogenase reaction. Acquisition of Ffz1 (2) and duplication of the MtDH gene (3) may have supported an increase in the flux toward mannitol production. In order to harvest the advantages of mannitol production also when glucose is the sole carbon and energy source a novel pathway (4) emerged converting fructose-6-P to fructose. (B) Novel pathway mediating the production of mannitol from glucose in W/S-clade yeasts; Hxk- Hexokinase, Glk- Glucokinase; Pgi- Phosphoglucose isomerase, Mtdh1- Mannitol dehydrogenase. Reactions involving M1pdh and Mpp are faded to indicate that they are absent in W/S-clade species.