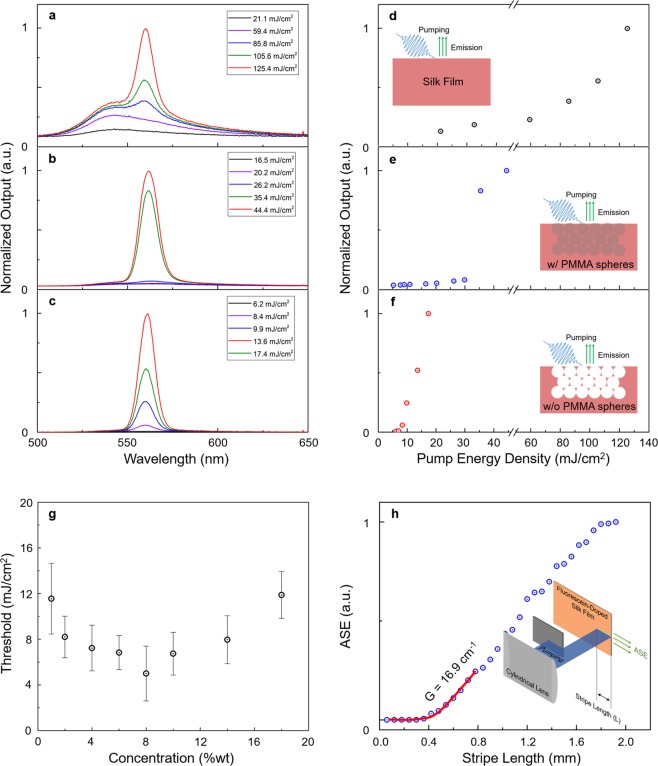
Figure 2.
Optical gain and ASE spectra from silk/dye films. (a–f), Pump-fluence dependences of the ASE emissions and threshold behaviors on the bulk silk/dye film: (a,d), the silk/dye film with the PMMA opal (b,e), and the silk/dye film with air voids after removing the PMMA opal (c,f). The concentration of the sodium fluorescein dye was 10 wt%. As RI contrast (Δn) of the opal structure was increased, the threshold was greatly reduced owing to the increased optical path. (g) The measured threshold pumping power of ASEs from the bulk dye/silk film with various concentrations of the sodium fluorescein dye. The error bar represents the standard deviation calculated using five data points at each concentration. (h) The variable stripe-length experiment to estimate the net modal gain of the bulk silk film mixed with sodium fluorescein. The concentration of sodium fluorescein was 8 wt%, and all spectra were excited at λ = 355 nm with a 25-ps pulse width.