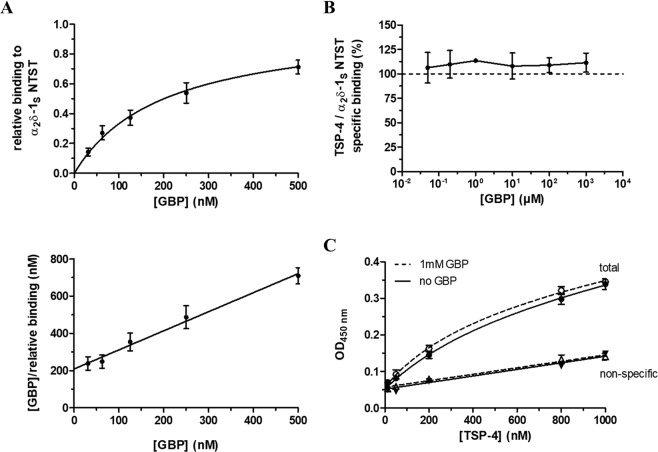
Figure 4.
GBP does not directly interfere with the binding of TSP-4 to α2δ-1S NTST in an ELISA-style ligand binding assay. (A) Surface plasmon resonance (SPR) measurements of the binding of GBP to recombinant α2δ-1S NTST. The protein (10–15 µg/ml) was directly immobilised to CM5 sensor chips and GBP (31.25–500 nM) in PBS buffer, pH 7.4 containing 0.05% Tween 20 was passed over the chip at a flow rate of 30 μl/min. Shown are data of the relative GBP binding to α2δ-1S NTST (Top) obtained from single cycle kinetics protocol (mean values ± SEM of 4 independent experiments, Fig. S3). Each experiment was analysed by non-linear regression according to the equation RU/RUmax = [GBP]/(KD + [GBP]), where the ratio of the binding response and the maximum binding response, RU/RUmax, represents the relative binding at a given GBP concentration, [GBP], and KD is the dissociation constant of the two interaction partners. Data analysis yielded a value of KD = 219 ± 47 nM (mean value ± SEM, n = 4), with the linear shape of the Hanes-Woolf transformation (Bottom) showing equimolar binding of the two interaction partners. For the ELISA-style assay, the α2δ-1S NTST (10 µg/ml) protein was coated onto 96-well plates and incubated with either (B) TSP-4 (1,000 nM) in the absence and presence of increasing concentrations of GBP (0.05–1,000 µM), or (C) increasing concentrations of TSP-4 (12.5–1,000 nM) in the absence (full symbols) and presence (open symbols) of GBP (1,000 µM). The assay was carried out in the presence of 2 mM Mg2+ and bound TSP-4 was detected with TSP-4-specific antiserum. Specific binding was calculated by subtracting OD values of non-specific binding (triangles) from those of total binding (circles). Data in (B) and (C) represent mean values ± SEM of 2 to 3 independent experiments, each performed in duplicate. In (B) the OD values for specific binding of TSP-4 in the presence of GBP (0.05–1,000 µM) were normalised to those in the absence of GBP.