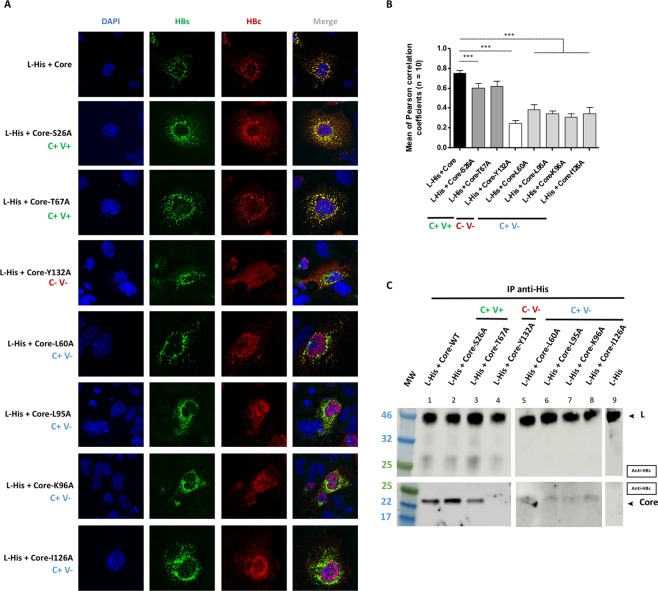
Figure 6.
Interaction between the L protein and the mutant core proteins. Huh7 cells were cotransfected with plasmids encoding the L-His protein and the WT core protein or one of the seven mutant core proteins. Three days post-transfection, cells were analyzed by immunolabeling and confocal microscopy, and co-IP was investigated with L-His as the bait. (A) Cells were double-stained with anti-HBs (in green) and anti-HBc (in red) antibodies, and nuclei were labeled with DAPI (in blue). As for the WT controls, a strong colocalization of the L-His and core proteins was observed with C+V+ mutants (core-S26A and coreT67A). Partial colocalization between the L-His and core proteins was observed with C+V− mutants (core-L60A, core-L95A, core-K96A, core-I126A) and no colocalization of L-His and core proteins was observed for the C-V- mutant (core-Y132A). (B) Histogram of r values, as previously described (***p value < 0.001). The capsid formation and secretion properties of each mutant are shown at the bottom of the figure. (C) Huh7 cell lysates were collected and 400 µg of total protein was subjected to IP with an anti-His antibody. The immunoprecipitated samples were subjected to immunoblotting and the membranes were probed with anti-HBs (IP) or anti-HBc (Co-IP) antibodies. The capsid formation and virion secretion properties of each of the mutant proteins are reported at the top of the figure. The C+V+ mutants were strongly co-immunoprecipitated with the WT L-His. Weak but detectable co-IP was observed with the C+V− mutants, whereas no signal was obtained with the C−V− mutant, as for the controls (simple transfection of each partner) (data not shown). All the blot acquisitions were processed in parallel and correspond to the same experiment.