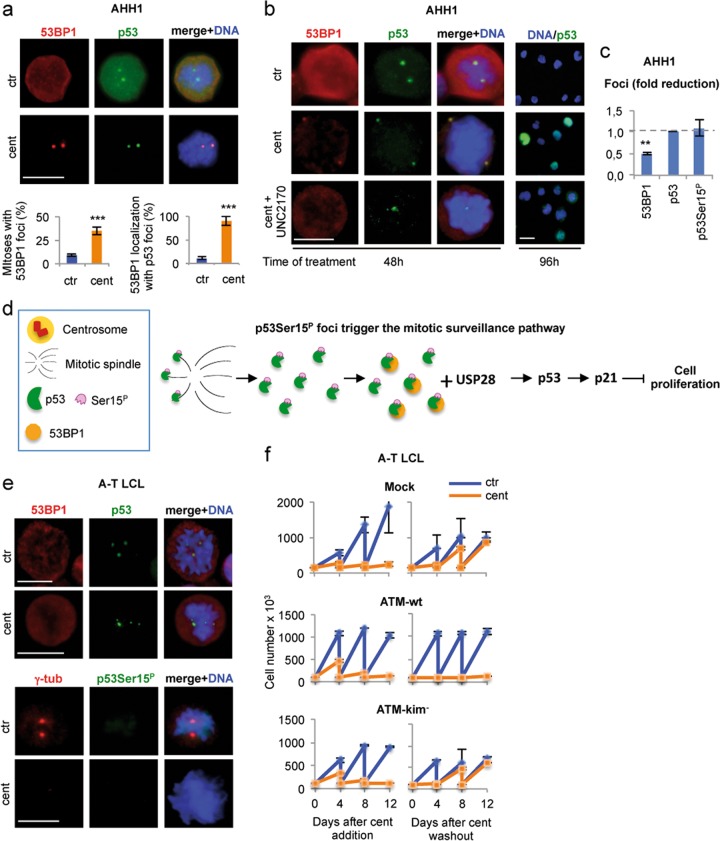
Fig. 7. p53Ser15P extra-centrosomal foci recruit 53BP1 and trigger the mitotic surveillance pathway.
a AHH1 cells were treated with centrinone for 48 h and double immunostained with anti-p53 and anti-53BP1 Abs. Representative IF images show that in response to centrosome-loss, mitotic cells have extra-centrosomal p53 foci that colocalize with 53BP1 foci. Histograms report the percentages of mitotic cells carrying 53BP1 foci and in which the 53BP1 foci colocalize with the p53 foci. b AHH1 cells were treated, for the indicated times, with centrinone with or without the 53BP1 inhibitor UNC2170 and analyzed by IF for the indicated proteins. Representative IF images of the 96 h time point show that UNC2170 prevented the p53 nuclear staining induced by centrinone treatment, supporting an inhibitory activity of the 53BP1 function in the mitotic surveillance pathway. Representative IF images of the 48 h time point show that UNC2170 reduces the formation of 53BP1 foci but not extra-centrosomal p53 foci. c Quantification of the IF analyses performed in (b) or not shown in the images (i.e., p53Ser15P foci) is reported in the histogram. The fold reduction induced by the addiction of UNC2170 on the indicated type of foci is shown. At least 30 mitotic cells per condition were analyzed. The results show that 53BP1 foci were significantly reduced while p53 and p53Ser15P foci were unmodified suggesting that their presence is independent of 53BP1. d Schematic representation of p53 working as sensor for the mitotic surveillance pathway in human nontransformed cells. Upon centrosome-loss, the p53Ser15P foci cannot reach the centrosome to be dephosphorylated (sensor shut down) to allow cell-cycle progression. Persistence of p53Ser15P foci recruit 53BP1 and trigger the mitotic surveillance pathway. In this context, p53 acts both upstream (p53Ser15P foci) and downstream (p53 transcription factor activating p21) the 53BP1/USP28 signaling axis. e To verify whether the ATM-dependent p53S15P has a role in the formation of the 53BP1 foci, centrinone treatment and IF analyses were performed on ATM-defective cells (A-T LCL) as above. Representative IF images show that, after centrosome-loss, extra-centrosomal p53 foci were detectable but they were not phosphorylated at Ser15 and 53BP1 did not form foci that colocalize with the p53 foci. Scale bars, 10 µm. f Cell passaging assays were performed, as in Fig. 6a, with A-T LCL and with A-T LCL reconstituted with ATM-wt and a kinase defective mutant, ATM-kim-. Centrinone treatment of A-T LCL did not irreversibly arrest the cell cycle, as shown by cell proliferation after centrinone washout. However, expression of ATM-wt, but not ATM-kim-, restored the capacity of cells to irreversibly exit from the cell cycle