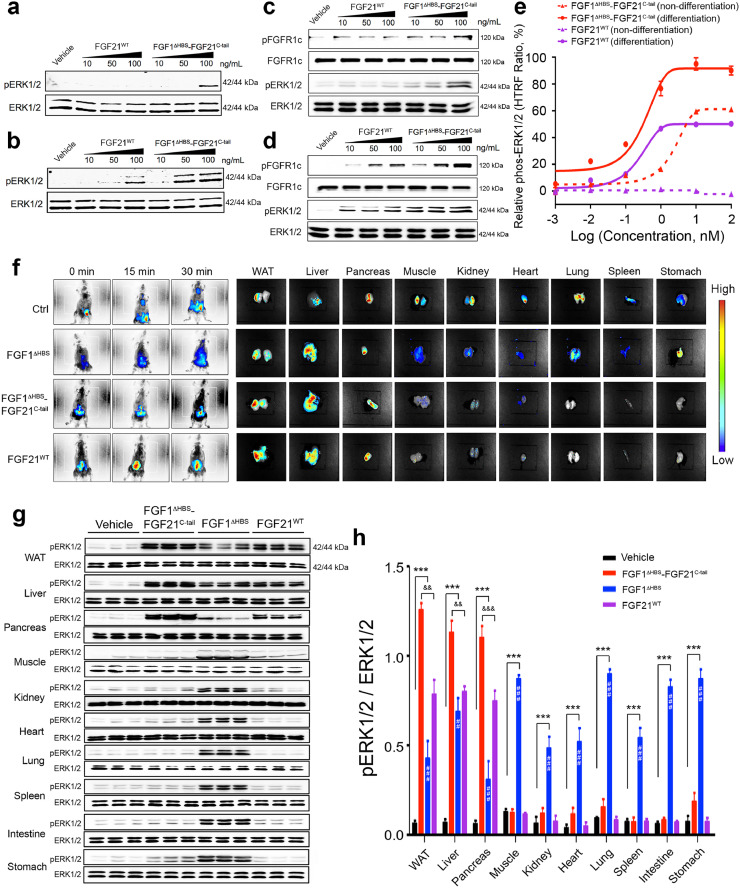
Fig. 4.
. βKlotho promotes signalling by the FGF1ΔHBS-FGF21C-tail chimera
(a-d) Western blot analyses showing dose-dependent phosphorylation of ERK1/2 induced by FGF21WT and FGF1ΔHBS-FGF21C-tail in BaF3 cells expressing FGFR1c alone (a), BaF3 cells co-expressing FGFR1c and βKlotho (b), and dose-dependent phosphorylation of FGFR1c and ERK1/2 induced by FGF21WT and FGF1ΔHBS-FGF21C-tail in undifferentiated (c) and differentiated (d) 3T3L1 adipocytes. (e) Relative values of ERK1/2 phosphorylation in undifferentiated and differentiated 3T3L1 adipocytes induced by a range of concentrations of FGF21WT and FGF1ΔHBS-FGF21C-tail. n = 3/concentration group. (f) Left hand panels: Distribution of Alexa 647 Fluor-labeled FGF1ΔHBS-FGF21C-tail, FGF21WT and FGF1ΔHBS proteins in C57BL/6 J mice at 0, 15 and 30 mins post-intraperitoneal injection (0.5 mg/kg body weight). Right hand panels: Ex vivo fluorescence imaging of the indicated organs harvested from the same mice. Injection with fluorescent dye alone was used as a control (Ctrl). Vertical scale at right shows colour correspondence with fluorescent intensity. (g) Western blot analyses of ERK1/2 phosphorylation in lysates prepared from WAT, liver, pancreas, muscle, kidney, heart, lung, spleen, small intestine and stomach from C57BL/6 J mice 30 min after subcutaneous injection with PBS (vehicle), FGF1ΔHBS-FGF21C-tail, FGF1ΔHBS or FGF21WT (0.5 mg/kg body weight). For each tissue, an ERK1/2 antibody was used as a loading control. (h) Quantitation of western blot data from (g) using Image J software. Data are presented as mean +/- SEM (n = 6). ***p<0.001, FGF1ΔHBS, FGF21WT and/or FGF1ΔHBS-FGF21C-tail vs vehicle; ##p<0.01, ###p<0.001, FGF1ΔHBS vs FGF1ΔHBS-FGF21C-tail; &&p<0.01, &&&p<0.001, FGF21WT vs FGF1ΔHBS-FGF21C-tail, unpaired t-test.