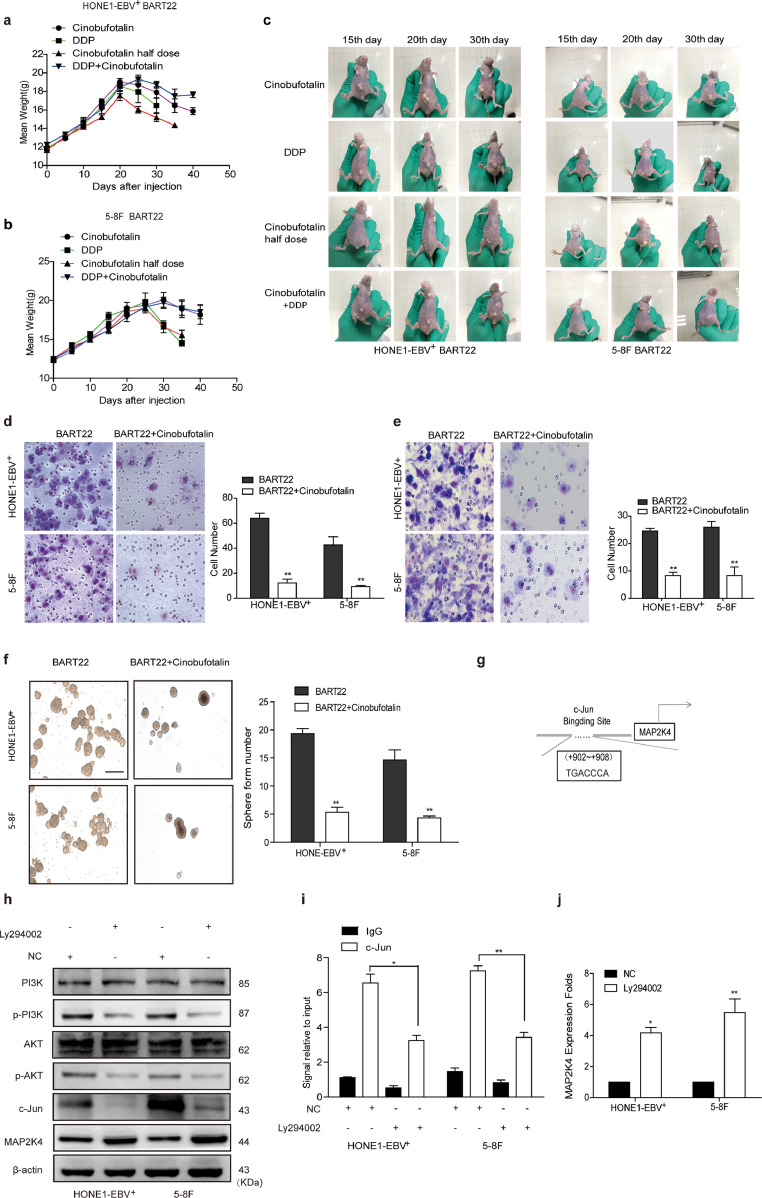
Fig. S7.
Related to Fig. 6. Cinobufotalin reversed EBV-miR-BART22-induced DDP resistance by inducing the expression of MAP2K4.
(a)(b) A fitted curve was used to determine the weight of each group. (c)Animals were divided into four groups: cinobufotalin, DDP, half-dose cinobufotalin, and DDP + cinobufotalin groups (each group: N = 10). Xenograft tumors are shown for each group at different days. (d–e) Migration and invasion were measured by Transwell and Boyden Chamber assays in HONE1-EBV+-BART22 and 5-8F-BART22 cells with Cinobufotalin treatment. (f) The sizes (left panel) and number of spheres (right panel) were examined in miR-BART22-overexpressing NPC cells with the treatment of cinobufotalin; three independent experiments were performed. Original magnification, ×100, scale bar, 200 μm; mean ± SD, *P < .05, **P < .01, ***P < .001. (g) Bioinformatics analysis to identify the binding sites of c-Jun within promoter of MAP2K4. (h) Western blot analysis of PI3K, p-PI3K, AKT, p-AKT, c-Jun, MAP2K4 expression in NPC cells with Ly294002 treated, GAPDH served as controls. (i) ChIP analysis of c-Jun binding to the transcriptional regulatory region of MAP2K4 in HONE1-EBV+ and 5-8F cells with Ly294002 treated. (j) qPCR analysis of MAP2K4 mRNA level in NPC cells with Ly294002 treated. All data are presented as the mean ± SD. *P < .05, **P < .01, Experiments were repeated three times.