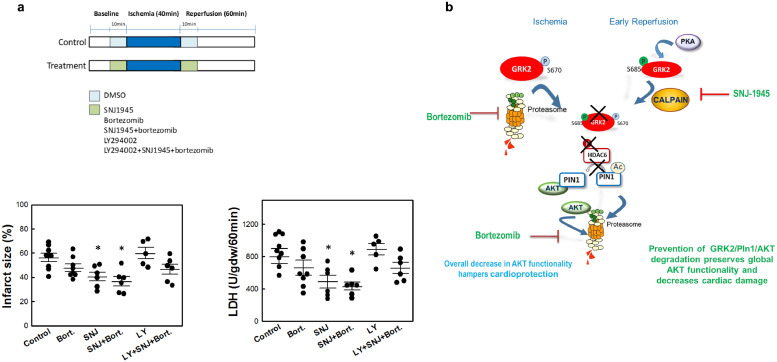
Fig. 8.
Cardiac ischemia-reperfusion injury is attenuated by combined-inhibition of proteasome and calpain activities. (A) Isolated rat hearts were treated during the 10 min prior to ischemia (40 min) and the first 10 min of a total period of 60 min reperfusion with the indicated combinations of the calpain inhibitor SNJ-1945 (SNJ, 10 μM), the proteasome inhibitor Bortezomib (BZ) (10 μM) and the PI3K inhibitor LY-294002 (10 μM).After the reperfusion period, total LDH released during reperfusion (expressed as units of activity released per gram of dry weight during the first 60 min of reperfusion, U/gdw/60 min) and infarct size (expressed as the percentage of ventricular mass in the different experimental groups) were determined as detailed in Methods. Data are the mean ± SEM, n = 6–9 rats per condition. *p < .05 vs untreated I/R control group [1-way ANOVA and Tukey's post-hoc test]. (B) Scheme of the molecular mechanisms underlying GRK2/Pin1/AKT degradation during myocardial ischemia and early reperfusion. See text for details.