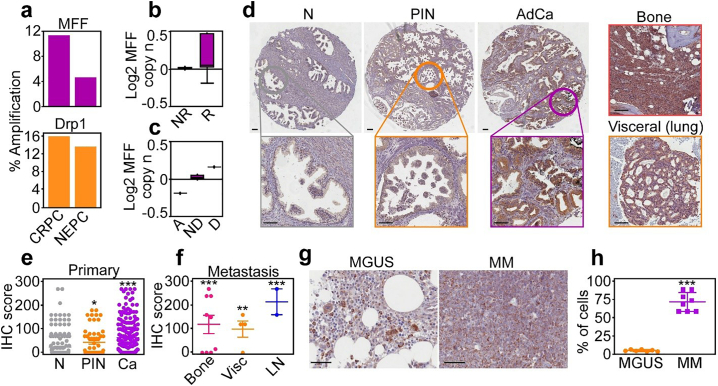
Fig. 1.
MFF overexpression in cancer. (a) Amplification of MFF and Drp1 in prostate cancer (77 patients, 107 samples). CRPC, castration-resistant prostate cancer; NEPC, neuroendocrine prostate cancer. (b) TCGA correlation (n = 380) between MFF expression and prostate cancer progression. NR, no recurrence at 5 years; R, recurrence at 5 years. (c) TCGA correlation (n = 380) of MFF expression (log MFF copy number) and prostate cancer survival. A, alive at 5 years; ND, alive with no evidence of disease at 5 years; D, dead with disease at 5 years. (d) MFF expression by immunohistochemistry in a patient cohort of localized and metastatic prostate cancer (n = 192). N, normal; PIN, prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia; AdCa, adenocarcinoma. Insets, image magnification of selected regions. Right, MFF expression in prostate cancer metastases to bone or lungs. Scale bar, 100 μm. (e and f) Quantification of MFF expression by immunohistochemistry (IHC) in primary (e) or metastatic (f) prostate cancer. *, p = .01; **, p = .003; ***, p < .0001 (by two-sided unpaired t-test; all compared to normal prostate). Vis, visceral; LN, lymph nodes. (g and h) MFF expression in representative patient samples of Monoclonal Gammopathy of Uncertain Significance (MGUS, n = 7) or Multiple Myeloma (MM, n = 8) by immunohistochemistry (g) and quantification of IHC score (h). Scale bar, 50 μm. ***, p < .0001 (by two-sided unpaired t-test).