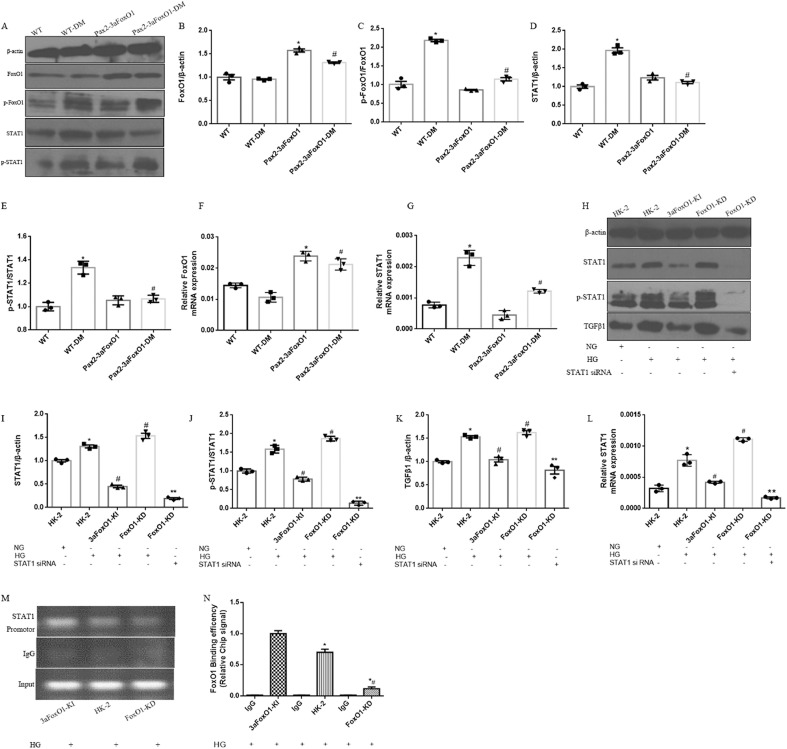
Fig. 9.
Effects of FoxO1 on HG-induced activation of STAT1 signaling pathway. (A) Representative western blot of FoxO1, p-FoxO1, STAT1 and p-STAT1 in diabetic mice kidneys. (B–E) Quantitative analysis of the densitometry of FoxO1, p-FoxO1, STAT1 and p-STAT1. (F–G) The mRNA levels of FoxO1 and STAT1 were assessed by RT-PCR. Data were shown as the mean ± SEM, *P < .05 vs. the WT mice; #P < .05 vs. the WT-DM mice. P values were determined by one-way ANOVA analysis. (H) Representative western blot of STAT1, p-STAT1 and TGFβ1 in HK-2 cells. (I–K) Quantitative analysis of the densitometry of STAT1, p-STAT1 and TGFβ1. (L) The mRNA level of STAT1 was assessed by RT-PCR. Data were shown as the mean ± SEM, *P < .05 vs. HK-2 cells incubated with NG; #P < .05 vs.HK-2 cells incubated with HG; **P < .05 vs. FoxO1-KD incubated with HG. P values were determined by one-way ANOVA analysis. (M) Nuclear extracts in HK-2, 3aFoxO1-KI and FoxO1-KD cells were immunoprecipitated with anti-FoxO1 antibody or IgG. (N) Quantitative analysis of the results of ChIP assay. IgG from rabbit served as a control. Data were shown as the mean ± SD, *P < .05 vs. 3aFxoO1-KI cells incubated with HG; #P < .05 vs. HK-2 cells incubated with HG. P values were determined by one-way ANOVA analysis.