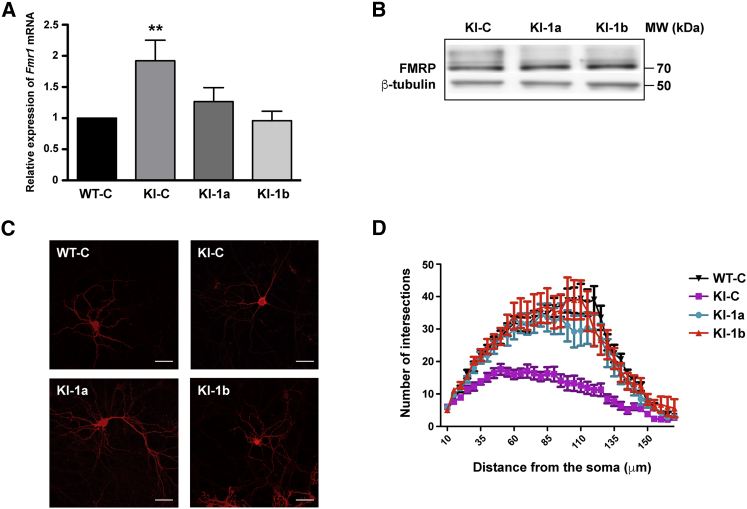
Figure 1.
Role of Fmr1 mRNA Levels in Dendritic Arborization
(A) RNA was prepared from cultured WT and knockin-CGG (KI-CGG) neurons transduced with the control (C) shRNA or two different shRNAs directed against Fmr1 mRNA (1a and 1b). The level of Fmr1 mRNA was measured by qRT-PCR using specific primers. Ten different experiments have been carried out for each transduced lentivirus, and a reduction of Fmr1 levels was observed by using both shRNAs. Results are presented as mean ± SEM; one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test, **p < 0.01. (B) Representative western blot analysis of cell cultures of cortical neurons transduced with C, 1a, or1b shRNAs. FMRP (70 kDa) and β-tubulin (50 kDa) were revealed with specific antibodies. (C) Image of WT and KI-CGG cortical neurons transduced with lentiviruses expressing C, 1a, or 1b shRNAs. Scale bars: 20 μm. (D) Sholl analysis of WT and KI cultured mouse cortical neurons transduced with C or 1a or 1b shRNAs. Reduced arborization of KI-CGG neurons is rescued by Fmr1 knockdown. Two-way ANOVA was used to compare KI-C and 1a treatments: genotype F(2; 1,527) = 227.9, p < 0.0001; treatment (34; 1,527) = 34.12, p < 0.0001; interaction F(68; 1,527) = 3.067, p < 0.0001; two-way ANOVA was used to compare KI-C and 1b treatments: genotype F(2; 1,318) = 293.6, ****p < 0.0001; treatment F(34; 1,318) = 36.21, ****p < 0.0001; interaction F(68; 1,318) = 3,803, p < 0.0001.