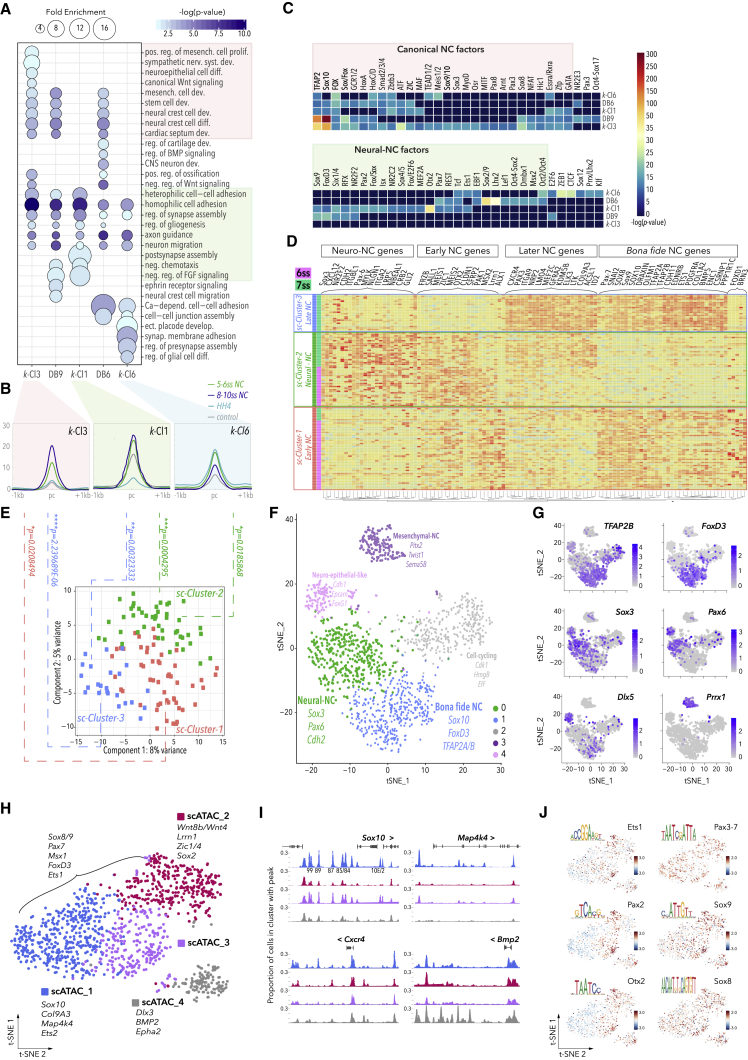
Figure 5.
Functional Dissection of k-Cluster Elements, Assignment to Single-Cell Transcriptomes, and Correlation with scATAC Clusters
(A) GO terms associated to k-means and DiffBind clusters. Fold enrichments were obtained using statistical overrepresentation test, p-values calculated with binomial distributions and Bonferroni correction for multiple hypothesis testing. K-Cl3 and DiffBind elements exclusively reflect canonical NC and mesenchymal cell development, and specific NC differentiation programs (sympathetic nervous system), while sharing roles in homophilic cell adhesion, gliogenesis, and axonogenesis with k-Cl6 and k-Cl1 (∗∗p < 0.01, Binomial test with Bonferroni correction, fold change >4). Only late-acting elements (k-Cl3, k-Cl1, and DiffBind 8-10ss) correlate to heterophilic cell-cell adhesion, while k-Cl6 elements play a role in early regulation of neuronal NC lineages, ectodermal placode formation, and cell-cell adhesion.
(B) Mean merged density profiles of k-Clusters.
(C) De novo TF binding motifs enriched in k-means and DiffBind clusters were identified using Homer. Binominal p-testing was used to determine motifs with p < 1 × 10−11.
(D) scRNA-seq heatmap visualizing hierarchical clustering of single NC cells at 6-7ss (total 124 cells, 74 6ss, and 63 7ss), sc-Cluster-1 (early NC, in red), sc-Cluster-3 (late NC, in blue), sc-Cluster-2 (neuronal-NC, in green). Top 50 differentially expressed genes are shown.
(E) PCA of top 100 genes from scRNA-seq. p values reflecting statistical significance of the single cell RNA-seq and k-means cluster associations were calculated using two-tailed hypergeometric test.
(F) tSNE plot depicting clustering of1509 NC cells at 7ss obtained by 10X Chromium scRNA-seq.
(G) Genes enriched in distinct clusters are labeled.
(H) Clusters of cells with differential chromatin accessibility as determined by scATAC.
(I) Chromatin accessibility patterns at differentially regulated loci. Colors correspond to (H).
(J) Enriched TF motifs across scATAC clusters.