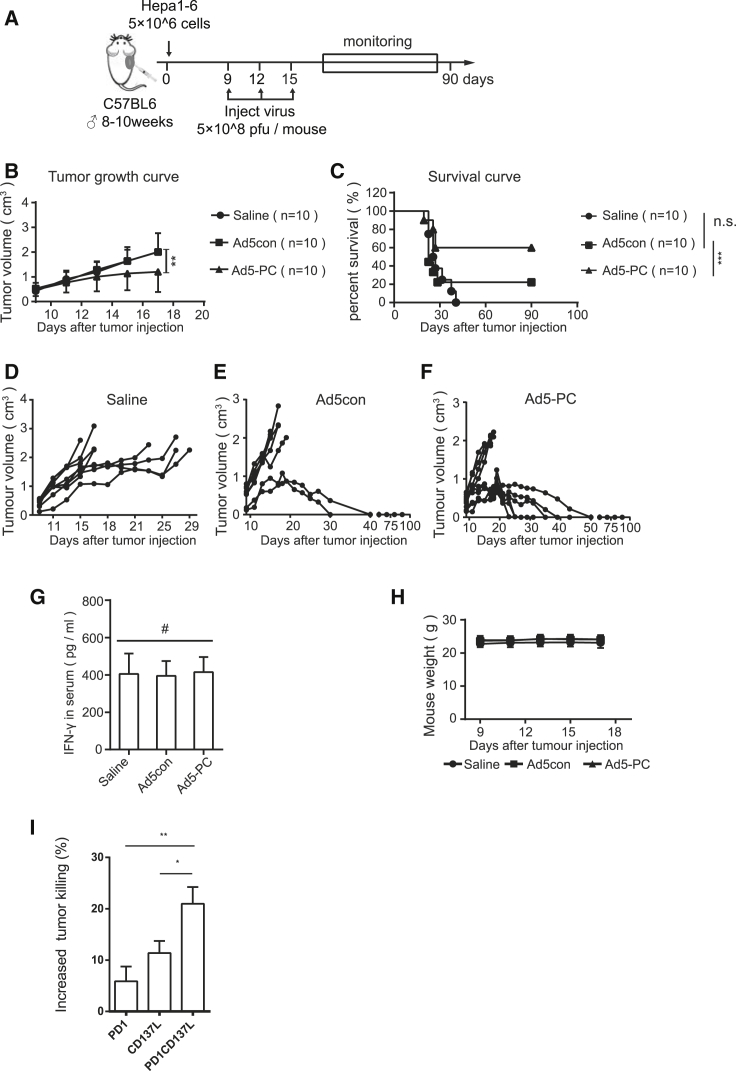
Figure 5.
Ad5-PC Attenuates Tumor Growth in a Subcutaneous HCC Murine Model
Male C57BL/6 mice were subcutaneously inoculated with 5 × 106 Hepa1-6. Recombinant adenovirus (5 × 108 PFUs/mouse) was locally injected when the tumor volume reached 0.4 cm3. The tumor volume and mouse weights were monitored, and the mice were considered to have died when the tumor volume reached 2 cm3. (A) Schematic diagram of the experimental setup for adenovirus therapy in solid tumors. Tumor volumes (B) and survival curves (C) of mice with or without treatment of recombinant adenovirus were determined. (D–F) Volume for each tumor in the group of mice treated with (D) saline, (E) Ad5con, or (F) Ad5-PC. (G) On day 14, the concentrations of sPD-1CD137 and IFN-γ in plasma were determined by ELISA. (H) Mouse weights were determined at the indicated time points. (I) Splenocytes and Hepa1-6 were mixed at a ratio of 5:1, in the presence of purified PD1, CD137L, or fusion protein PD1/CD137L, respectively. The number of Hepa1-6 cells was reflected by the bioluminescence intensity. Data shown are the means ± SD. #Not significant; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.