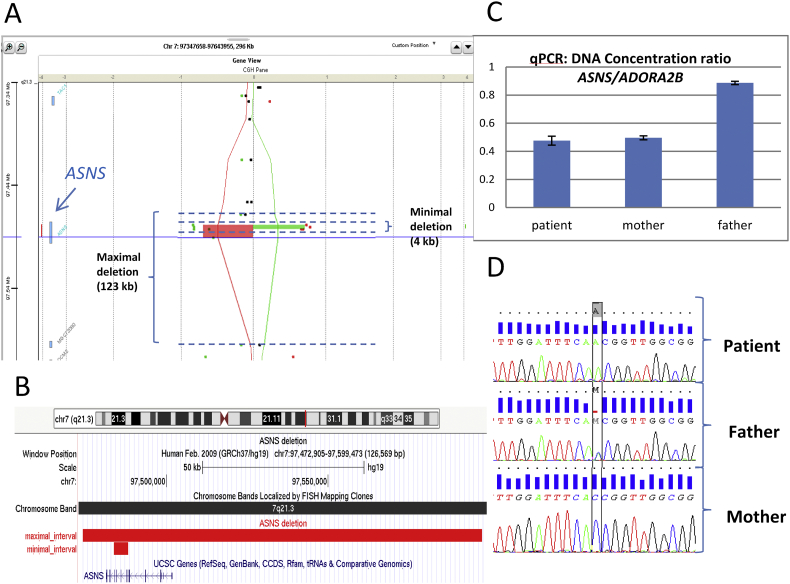
Fig. 1.
Deletion in array-CGH analysis confirmed by qPCR and pathogenic variant in Sanger sequencing in ASNS in our patient and her parents.
A: A view of the heterozygote deletion involving the ASNS gene detected by array-CGH using a dye-swap method. Patient and control are compared twice with the dye assignment reversed in the second hybridization. In the first assignment, patient is compared to the control (red line and rectangle) and in the second assignment control is compared to the patient (green line and rectangle). A maximal 123 kilobases (kb) deletion with boundaries from 97,474,170 to 97,597,701 and a minimal 4 kb deletion from 97,483,869 to 97,488,230 were considered because of the poor density of probes within the region. B: A UCSC view with the interval of the maximal and the minimal deletion, both concerning ASNS coding sequences. C: Quantitative PCR of DNA concentration ratio between ASNS and a reference gene (ADORA2B) confirming the presence of the deletion in our patient inherited from her mother. D: Genetic chromatograms showing the hemizygous mutation in exon 3 c.144C > A; p.His48Gln in our patient inherited from her father. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)