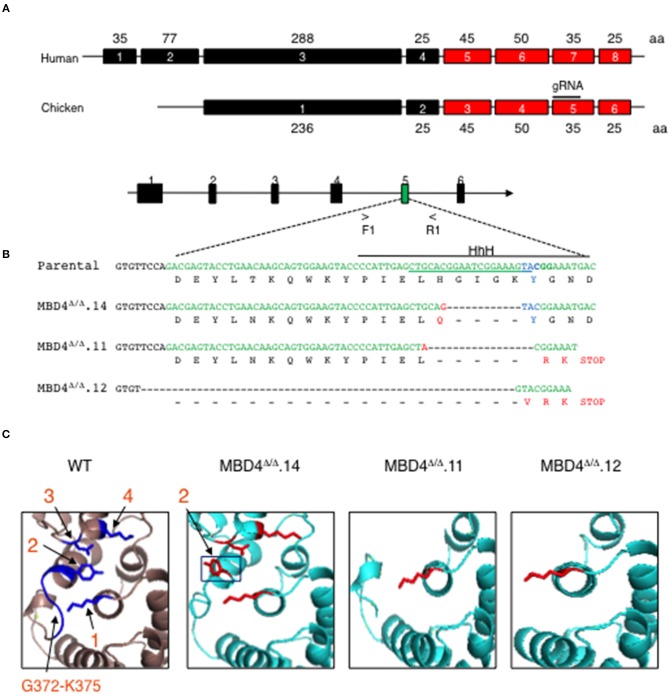
Figure 2.
CRISPR/Cas9 genome generated deletions in the chicken MBD4 glycosylase domain of DT40 cells. (A) Schematic of human and chicken MBD4 exons (not drawn to scale) Exon numbers are given in boxes with amino acid (aa)s in each exon labeled. The glycosylase domain is highlighted in red and guide (g) RNA in chicken exon 5 annotated. (B) Schematic of Mbd4 gene showing exon 5 targeted by CRISPR/Cas9 editing (not drawn to scale). Mbd4 PCR amplification using primers F1 and R1 was used to identify indels. The gRNA sequence is underlined along the parental DNA (upper) strand and catalytic aa Y376 (lower strand) shown in blue. HhH motif is displayed by solid black line. Deletions in the Mbd4 gene for clones Mbd4Δ/Δ.14 (12 bp deletion), Mbd4Δ/Δ.11 (17 bp deletion), and Mbd4Δ/Δ.12 (62 bp deletion), as compared to the parental sequence (aa 357–379) and predicted aa sequences are shown. (C) The predicted 3D structure of the chicken MBD4 glycosylase domain (aa262-416) is compared to mutated clones, as indicated. Critical amino acids in WT MBD4 are numbered K304 (1), Y376 (2), D396 (3), and K398 (4). Amino acids G372-K375 are present only in WT.