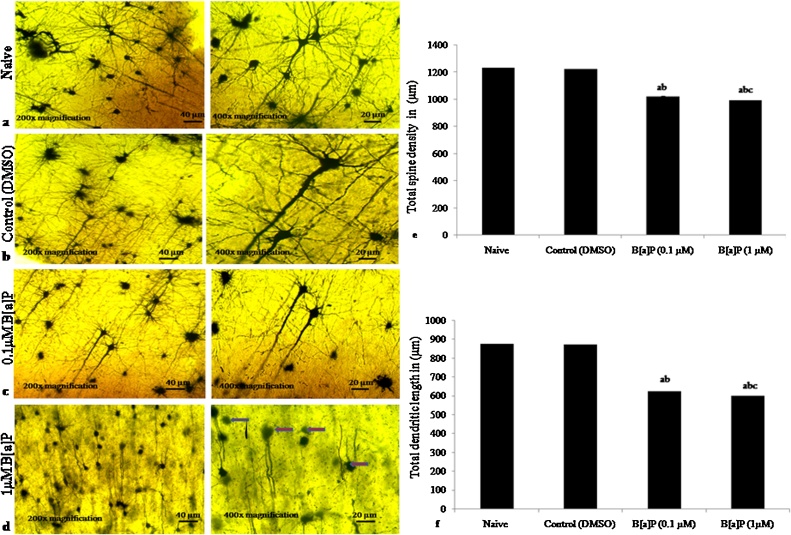
Fig. 5.
Effects of early adolescence intraperitoneal administration (i.p.) of B[a]P and measurement of dendrite morphology and spine density in adult wistar rats using Golgi-cox staining. Representative images of Golgi-Cox staining sections of adult rat hippocampus in naïve [Fig. 5:(a)], control (DMSO) [Fig. 5:(b)] and two different dose levels, B[a]P (0.1 ⁎μM) [Fig. 5:(c)] and B[a]P (1μM) [Fig. 5:(d)] of adult after intraperitoneal administration (i.p.) to early adolescence male wistar rats with (Scale bar = 100 μm) at 20x magnifications and (Scale bar =20 μm) at 40x magnifications (Fig.5 a).
Histogram representing alteration of spine length, spine number, density [Fig. 5: (e)] and dendrite nodes of neurons in hippocampus of two different dose levels of B[a]P treated groups [Fig. 5:(f)]; (0.1 μM/10 μl) and B[a]P (1 μM/10 μl) as compared to naïve and control (DMSO) groups. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM, n = 6. ‘a’ denotes p < 0.05 when compared to naïve group, ‘b’ denotes p < 0.05 when compared to control (DMSO) group and ‘c’ denotes p < 0.05; when compared to B[a]P (0.1 ⁎μM).