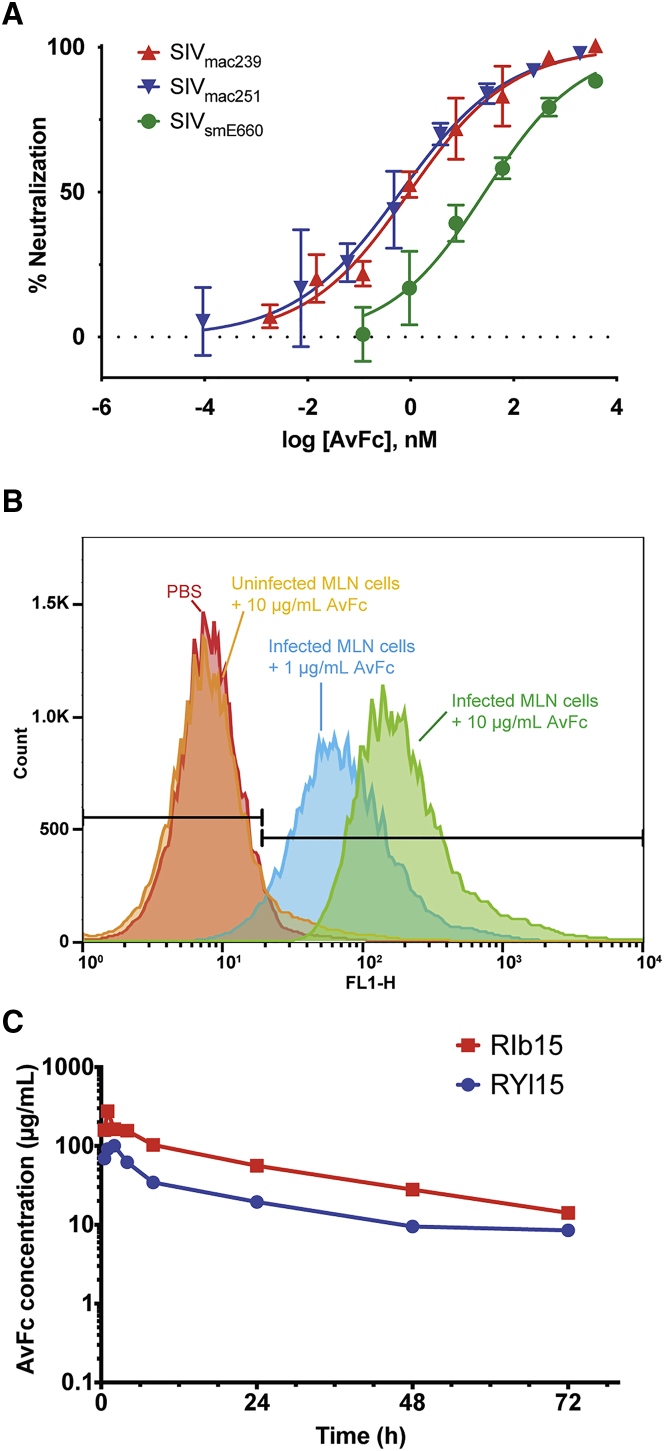
Figure 6.
SIV-Neutralizing Activity, SIV-Infected Cell Binding, and Macaque Subcutaneous Administration of AvFc
(A) Neutralization of SIV by AvFc. SIV strains smE660, mac239, and mac251 were propagated in CEMx174 cells. TZM-bl cells were infected with SIV in the presence of a vehicle control or serially diluted AvFc starting from 300 μg/mL (for mac239 and smE660) or 150 μg/mL (for mac251) at 37°C for 2 days. RLUs were converted to percent infection using the values from the no-drug control wells as 100% infection. AvFc neutralized SIVsmE660, SIVmac239, and SIVmac251 with IC50 values of 15.3, 6.6, and 1.8 nM respectively. Representative data from 3 independent experiments are indicated. (B) AvFc binding to rhesus macaque MLN cells. As shown, AvFc bound to SIVmac239-infected cells but not non-infected ones. (C) Pharmacokinetics of AvFc in rhesus macaques. A single bolus dose of 21 mg administered to each of two female macaques was well tolerated, with an average half-life of 27.7 h. Peak concentration occurred between 1 and 2 h post-injection.