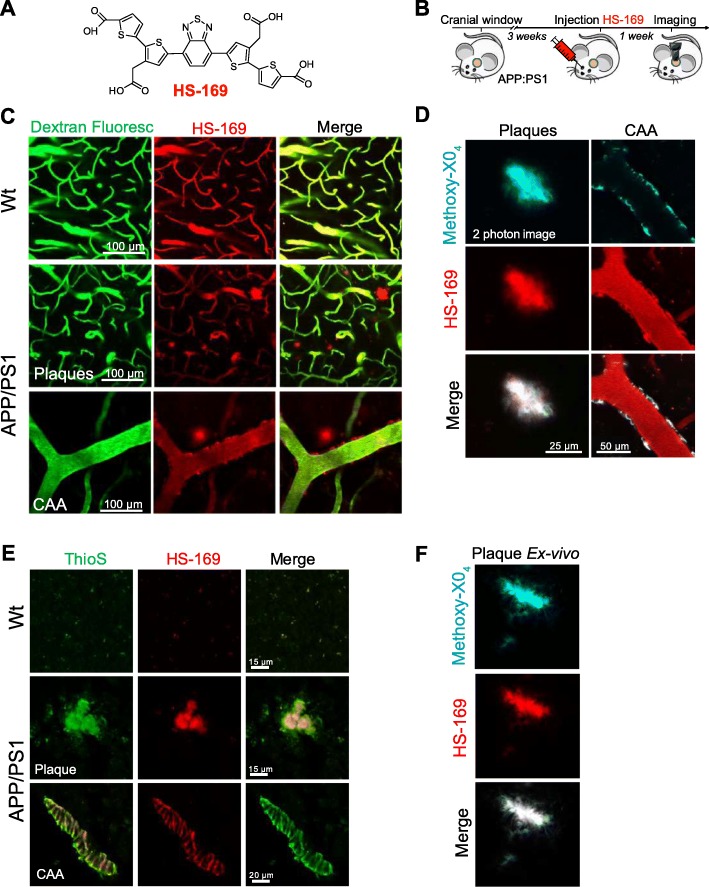
Fig. 3.
HS-169 binds to amyloid plaques and CAA in the APP:PS1 Tg mouse and can be detected with multiphoton microscopy. a. HS-169 molecule. b. Experimental procedure to characterize HS-169 in the mouse brain in vivo. APP:PS1 Tg mice and Wt littermates with a cranial window already implanted were injected with HS-169 via retro-orbital and subjected to intravital multiphoton microscopy. c. Representative in vivo multiphoton microscopy images of HS-169 in Wt (top) and APP:PS1 Tg mouse (middle and bottom). Pictures show Dextran Fluorescein (green), amyloid plaques and CAA labelled with HS-169 (red) and merge of both channels. Scale bar represents 100 μm and applies to all pictures. n = 3 Wt and 10 APP:PS1 Tg mice. d. In vivo validation of HS-169 labelling amyloid core plaques. HS-169 and Methoxy-X04 where co-injected in the same APP:PS1 Tg mouse. Colocalization of both dyes is shown. Representative of n = 3 APP:PS1 Tg mice. e. Post-mortem validation of HS-169 labelling amyloid beta pathology in the mouse brain. ThioS staining was used to probe colocalization with amyloid plaques and CAA in the APP:PS1 Tg mice (bottom) and compared to Wt littermates (top). HS-169 was injected via retro-orbital and the mice were euthanized 24 h later. Brains were sliced in a cryostat and incubated with 0.005% ThioS in EtOH. Colocalization of both dyes can be appreciated. f. Co-staining of Methoxy-X04 and HS-169 ex vivo in the APP:PS1 tissue to confirm the colocalization observed in vivo