Fig. 8.
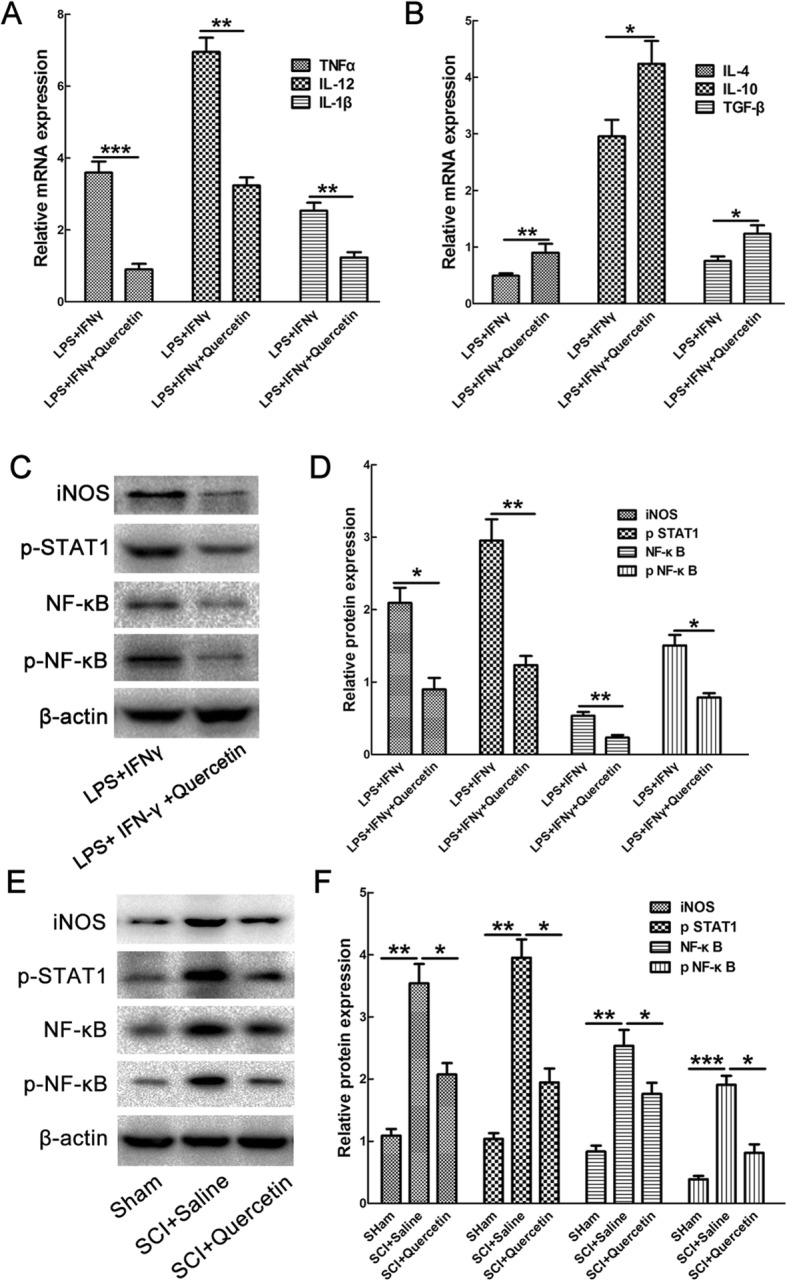
Effects of quercetin on M1 polarization of microglia and expression of pSTAT1, NF-κB, and pNF-κB. a, b The effect of quercetin on mRNA levels of M1 related TNFα, IL-12, IL-1β, and M2-related IL-4, IL-10, and TGF-β in M1 microglia. Note that quercetin significantly decreased mRNA levels of TNFα, IL-12, and IL-1β, while increased mRNA levels of IL-4, IL-10, and TGF-β. Data were expressed as mean ± SEM of three independent experiments. c Expression of iNOS, pSTAT1, NF-κB, and pNF-κB in microglia treated by LPS + IFN-γ in the presence or absence of quercetin. d Quantification of protein levels. β-actin was used as a loading control. Data were expressed as mean ± SEM of three independent experiments. e Expression of iNOS, pSTAT1, NF-κB, and pNF-κB in sham, saline, or quercetin-treated rats at 10 dpi after SCI. f Quantification of protein levels. Data were expressed as mean ± SEM of 6 rats. Differences among groups were determined with unpaired two-tailed t test (a, b, d) or one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey post-hoc test (f). *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001
