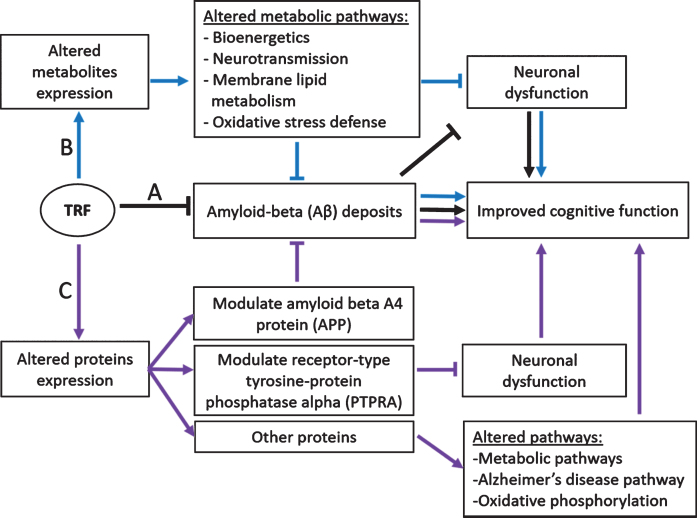
Fig.4.
Proposed mechanisms of TRF action in improving cognitive function in AβPP/PS1 mice. Aβ deposits, altered metabolites, and proteins expression cause neuronal dysfunction leading to cognitive impairment. A) TRF reduces Aβ deposition and improves cognitive function (black arrow) [17]. B) TRF modulates metabolic pathways, reducing neuronal dysfunction, and improves cognitive function (blue arrow) [18]. C) TRF modulates amyloid beta A4 protein (APP) leading to reduced Aβ deposits and improved cognitive function. TRF also modulates receptor-type tyrosine-protein phosphatase alpha (PTPRA), reducing neuronal dysfunction, and improves memory. TRF may also improve memory by modulating other proteins involved in metabolic pathways, Alzheimer’s disease pathway, and oxidative phosphorylation (purple arrow). Figure modified from Durani et al. [18].