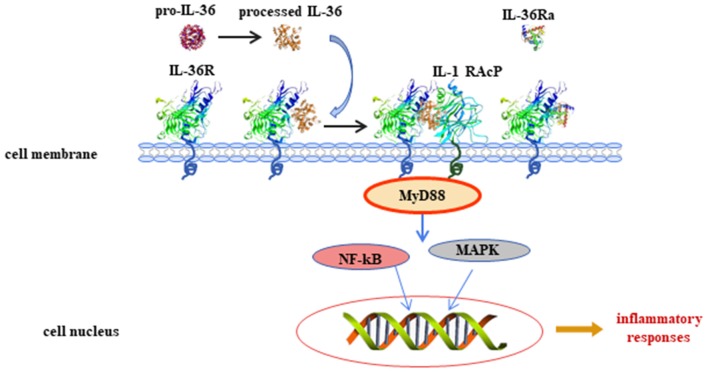
Figure 1.
Interleukin (IL)-36 signal pathways induce inflammatory responses. Pro-IL-36 cytokines are inactive proteins and require post-translational processing to fully unleash the pro-inflammatory activity. IL-36 agonists bind to heterodimeric receptor complexes, including IL-36 receptor (IL-36R) and co-receptor IL-1 receptor accessory protein (IL-1RAcP). Subsequently, the heterotrimer complex binds to adaptor protein myeloid differentiated protein 88 (MyD88), activating mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) and nuclear transcription factor kappa B (NF-κB) signaling cascade pathways, and regulates expression of target genes.