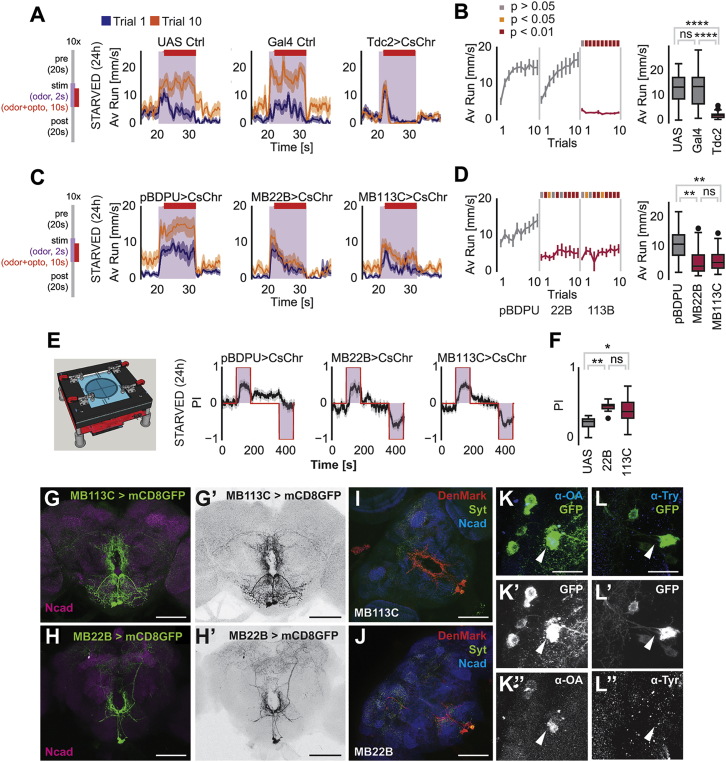
Figure 5.
A Subset of Octopaminergic Neurons Inhibit Odor Tracking
(A) Acute optogenetic activation of octopaminergic neurons. CsChrimson was expressed in octopaminergic neurons by Tdc2>UAS-CsChrimson (Controls: UAS Ctrl: +>UAS-CsChrimson, Gal4 Ctrl: Tdc2-Gal4>+). Running speeds during trial 1 and trial 10.
(B) Evolution of average running speeds for Tdc2>UAS-CsChrimson flies during odor exposure over trials. The boxplot displays the main group effect.
(C) Acute optogenetic activation of VPM neurons. MB22B harbors VPM3 and VPM4 neurons, whereas MB113C labels only VPM4 (Control: pBDPU-Gal4>UAS-CsChrimson). Running speeds during trial 1 and trial 10.
(D) Average running speeds for MB22B>UAS-CsChrimson and MB113C>UAS-CsChrimson flies during odor exposure. The boxplot displays the main group effect.
(E) Left: Scheme of optogenetic and olfactory behavioral test arena. Right: Average preference index during optogenetic activation of octopaminergic neurons under vinegar exposure.
(F) Activation of VPMs compared to genetic controls.
(G–J) Expression patterns and polarity of MB22B (H, H′, and J) and MB113C (G, G′, and J) split-Gal4 lines. SEZ (subesophageal zone); PEZ (periesophageal zone)
(K–L″) VPM4 neurons (MB113C>mCD8GFP) express octopamine.
For all analyses, statistical notations are as follows: ns, p > 0.05; ∗, p < 0.05; ∗∗, p < 0.01; ∗∗∗, p < 0.001; ∗∗∗∗, p < 0.0001. In all panels, error bars denote SEM.