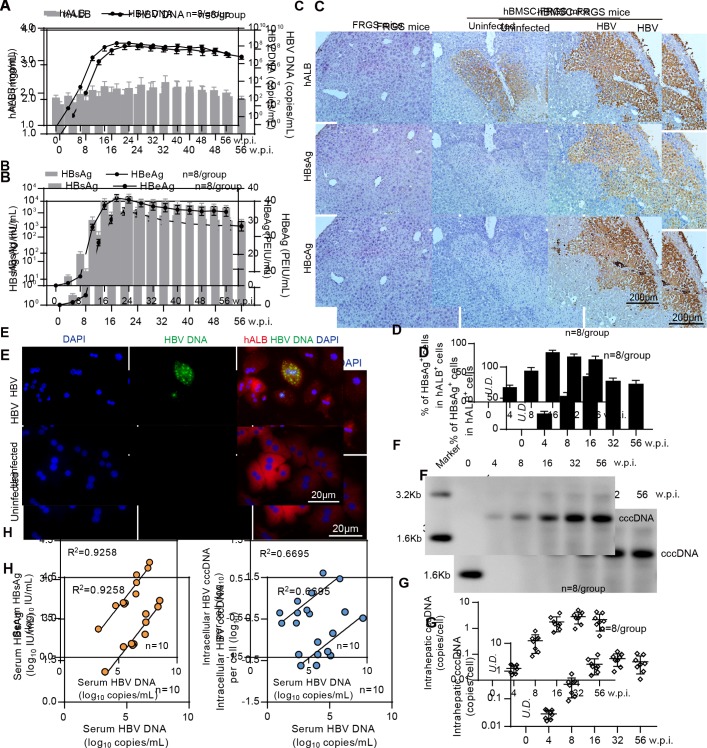
Figure 4.
Establishment of sustained HBV infection in human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-Fah-/- Rag2-/- IL-2Rγc-/- SCID (hBMSC-FRGS) mice. (A) Serum human albumin (hALB) (grey columns), HBV DNA (black lines), (B) hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) (grey columns) and hepatitis B e antigen (HBeAg) (black lines) levels in hBMSC-FRGS mice inoculated with HBV (genotype C) from 0 to 56 weeks postinfection (w.p.i.) (n=8/group). (C) Immunohistochemistry (IHC) staining for hALB+, HBsAg+ and HBcAg+ cells of liver tissues collected from HBV-infected and uninfected hBMSC-FRGS mice and FRGS mice at 16 w.p.i. (bar=200 µm). (D) Statistical analysis of IHC images to determine the proportion of HBsAg+ cells in the population of hALB+ cells from 0 to 56 w.p.i. (n=8/group). (E) Fluorescence in situ hybridisation (FISH) analysis for HBV DNA in the population of hALB+ cells collected from HBV-infected hBMSC-FRGS mice and uninfected controls at 4 w.p.i. (bar=20 µm). Detection of intrahepatic HBV covalently closed circular DNA (cccDNA) levels in HBV-infected hBMSC-FRGS mice from 0 to 56 w.p.i. by (F) Southern blot and (G) quantitative reverse transcription PCR (qRT-PCR) (n=8/group). (H) Analysis of the correlation between the serum HBV DNA and serum HBsAg levels and the correlation between the serum HBV DNA and intracellular HBV cccDNA levels (n=10). PEIU, Paul Ehrlich Institute units.