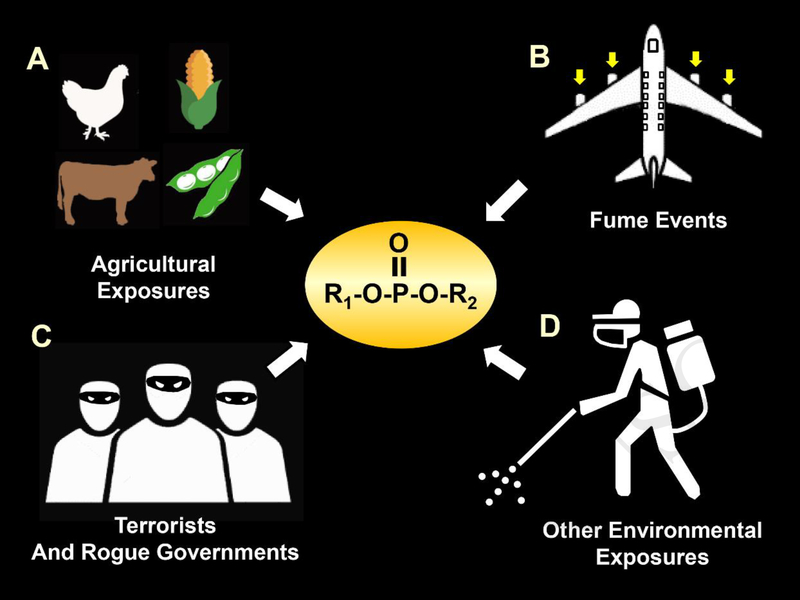
Fig 1.
Illustration of several representative sources of toxic exposures to OPs by humans and other non-target species. A. OP exposures in the agricultural setting, which may come from insecticides, anthelmintics, fungicides, and herbicides. B. OP exposures from terrorist attacks and chemical warfare assaults by rogue governments. C. Exposures as a result of “fume events” where the cabin air of an airplane can be contaminated with heated engine oil fumes that contain OPs. D. Exposures from insecticides used by public health officials to combat vector borne illnesses.