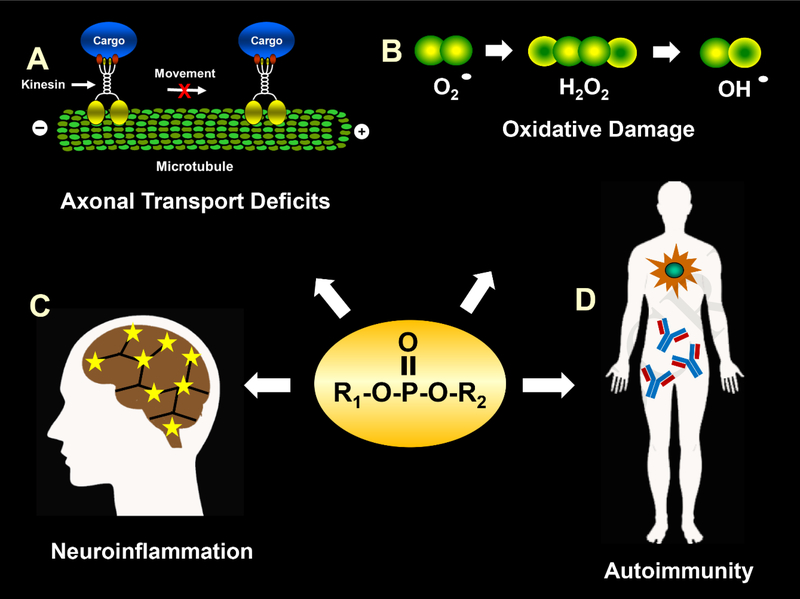
Fig 2.
Illustration of several representative physiological processes that may be affected by OPs to result in long-term deleterious health effects. A. OPs may impair axonal transport by altering the function of motor proteins such as kinesin and/or components of the neuronal cytoskeleton (e.g., microtubules). B. OPs can increase free radical formation and oxidative stress, which can lead to mitochondrial dysfunction and DNA damage to cells. C. OPs can lead to microglia activation and an increase in proinflammatory cytokines, which in turn may lead to neuroinflammation. D. OP exposure may lead to the generation of autoantibodies that target multiple proteins known to play important roles in both the structure and function of neurons including myelination and axonal transport.