Figure 3:
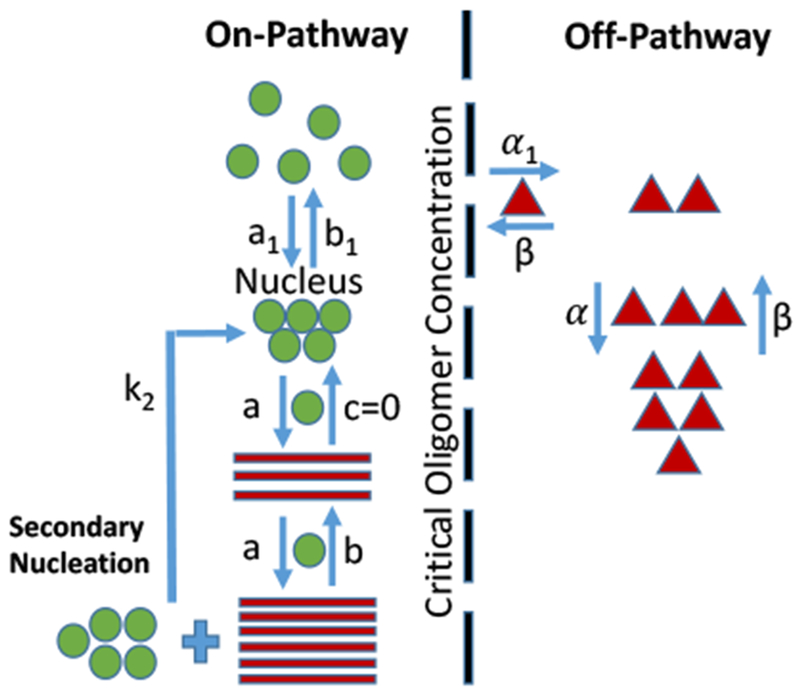
Schematic of the final coopertaive oligomer model. Monomers along the on-pathway are displayed with green spheres, where in addition to primary nucleation, secondary nucleation contributes to RFs seed formation. Within the on-pathway, N monomers associate cooperatively in one step to form a nucleus. Beyond the nucleus, fibril growth ensues (red bars), continuing till all monomers are consumed, progressively increasing the size of RFs. The irreversibility of RFs is indicated by the dissociation rate c = 0. The already existing RFs catalyze the formation of new ones through secondary nucleation with a rate constant k2. On the off-pathway, monomers first form the intermediate species, followed by final globular oligomeric species. gOs are metastable, dissolving into monomers that eventually end up in RFs along the on-pathway.
