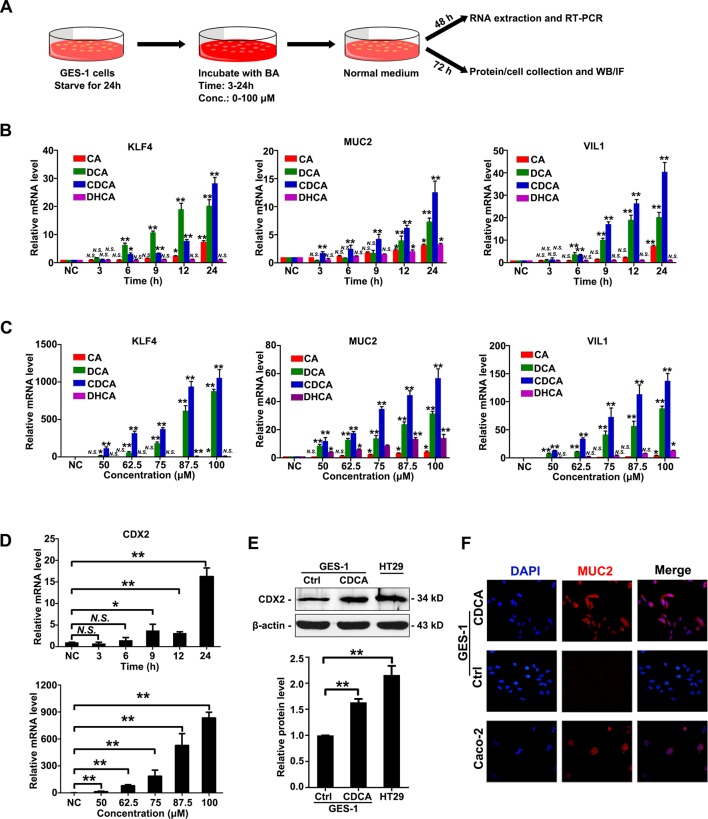
Figure 1.
Bile acids induced CDX2 and intestinal markers in gastric cells. (A) Workflow to examine the change of phenotype in gastric epithelial cell line (GES)-1 cells treated with bile acids. Fractions of bile acids: CA, DCA, CDCA and DHCA. Incubating time: 3, 6, 9, 12 and 24 hours at 50 µM; dosage: 50, 62.5, 75, 87.5 and 100 µM for 24 hours. (B) Expression of Krüppel-like factor 4 (KLF4), VILLIN (VIL1), MUCIN 2 (MUC2) were increased on stimulation of bile acids in a time-dependent manner. Incubating time: 3, 6, 9, 12 and 24 hours; dosage: 50 µM. (C) Expression of KLF4, MUC2 and VIL1 were increased on stimulation of bile acids in a dose-dependent manner. Incubating time: 24 hours; dosage: 50, 62.5, 75, 87.5 and 100 µM. (D) Top: messenger RNA (mRNA) levels of CDX2 was increased by CDCA treatment in a time-dependent manner. Incubating time: 3, 6, 9, 12 and 24 hours. Dosage: 50 µM. Bottom: mRNA levels of CDX2 was increased by CDCA treatment in a dose-dependent manner. Incubating time: 24 hours; dosage: 50, 62.5, 75, 87.5 and 100 µM. GAPDH RNA was used as internal control in qRT-PCR. (E) Protein levels of CDX2 in GES-1 cells treated with CDCA (100 µM) for 24 hours. HT-29 as a positive control. β-Actin levels were used as internal control. (F) MUC2 expression in GES-1 cells treated with CDCA (100 µM) for 24 hours. Caco-2 as a positive control. Means±SEM of a representative experiment (n=3) performed in triplicates are shown. *P<0.05; **p<0.01. N.S., not significant.