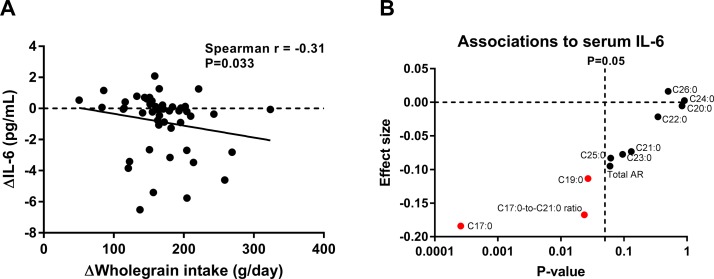
Figure 2.
Change in fasting serum concentrations of IL-6 was associated with whole grain intake. (A) ΔIL-6, designating change in serum concentrations during the whole grain period minus the change during the refined grain, was negatively associated with ΔWhole grain intake, designating difference in whole grain intake between the two periods, as calculated by Spearman’s rank correlation (n=47). (B) Serum concentrations of IL-6 were negatively associated with plasma AR homologues (biomarkers of whole grain intake) and in particular with the C17:0 homologue (p=0.0003) and the ratio of C17:0-to-C21:0 (p=0.024), indicating a specific association with intake of whole grain rye, as calculated by linear regression analyses adjusted for age and gender (n=50) (see also online supplementary table S6). AR, alkylresorcinol; IL-6, interleukin 6.