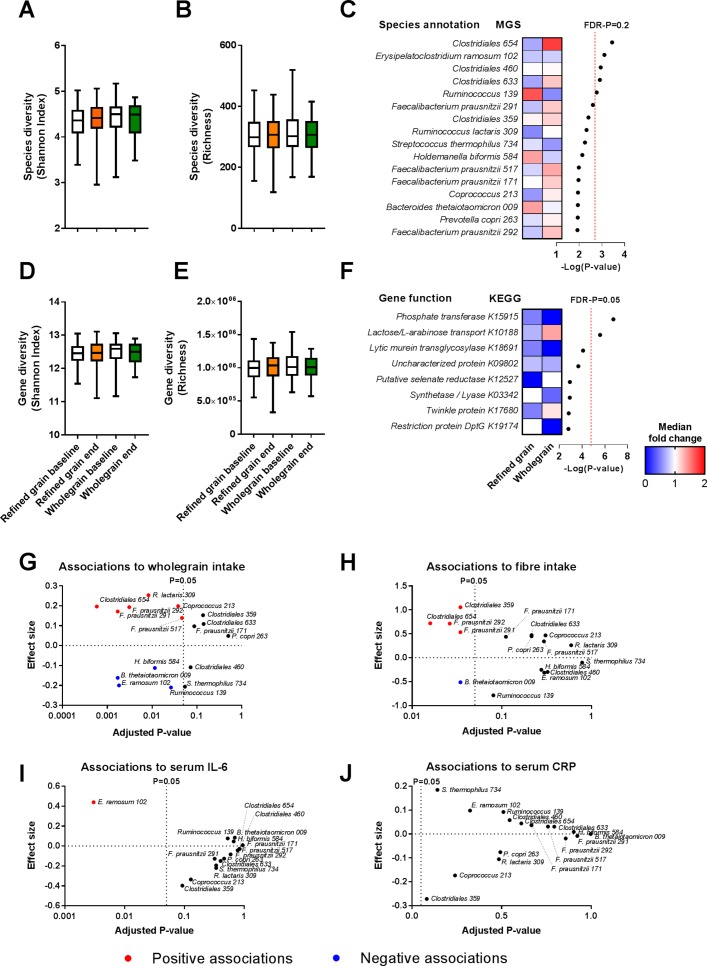
Figure 3.
Faecal microbiome composition did not differ between the two diets. (A) The subjects’ faecal microbial species diversity assessed by Shannon Index and (B) richness did not significantly differ between the two diets. Shown is the species diversity at baselines (white boxes) and at the end of the refined grain diet (orange boxes) and whole grain diet (green boxes). (C) Heatmap of the median fold changes in relative abundance of the individual MGSs during refined grain and whole grain diet, respectively. No MGSs changed significantly comparing the two periods. Of note, five species differed between diets with a FDR-P below 0.2 (red dotted line). (D) Gene diversity assessed by Shannon Index and (E) richness did not differ significantly between diets. Shown is the gene diversity at baselines (white boxes) and at the end of the refined grain diet (orange boxes) and whole grain diet (green boxes). (F) Heatmap of the median fold changes in relative abundance of the individual gene functions (KOs) during refined grain and whole grain diet, respectively. Two KOs differed significantly between diets with a FDR-P below 0.05 (red dotted line). Changes in microbiome composition were assessed by linear mixed model adjusted for age and gender followed by correction for multiple testing by the Benjamini-Hochberg approach (n=48) (see also online supplementary table S7 and S8). Among the bacterial species responding most to the intervention, several species were associated with (G) whole grain intake and (H) fibre intake, whereas only Erysipelatoclostridium ramosum was associated with (I) serum IL-6 concentrations and no species were associated with (J) serum CRP concentrations as assessed by the linear mixed model adjusted for age and gender followed by correction for multiple testing by the Benjamini-Hochberg approach (n=48) (see also online supplementary table S11). CRP, C-reactive protein; FDR-P, false discovery rate corrected p value; KEGG, Kyoto Encyclopaedia of Genes and Genomes; KO, KEGG orthologies; MGS, metagenomic species.