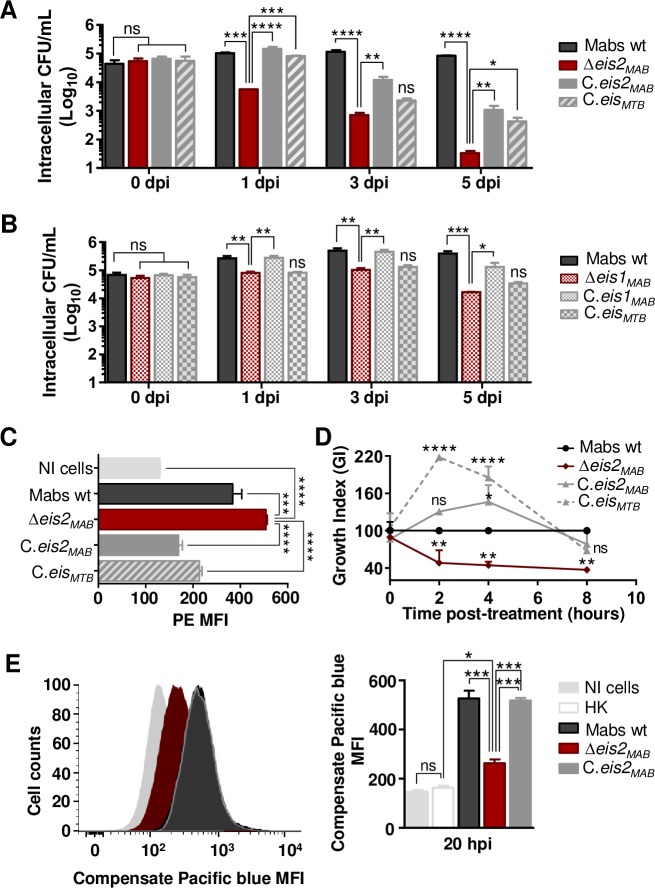
Fig 6. M. abscessus eis2 gene is essential for survival in Mϕ and shares functions with M. tuberculosis eis conversely to M. abscessus eis1.
(A) Intracellular survival of M. abscessus eis2 KO strain (Δeis2MAB) and complementation in Mϕ. (B) Intracellular survival of M. abscessus eis1 KO strain (Δeis1MAB) and complementation in Mϕ. Mϕ were infected at 10 MOI and colony forming unit (CFU) tests were performed at several times post-infection (0, 1, 3 and 5 dpi). (C) Control of ROS production by M. abscessus Eis2. ROS production by Mϕ was assessed by flow cytometry with the Mitosox Red kit, 15 min post-infection at 50 MOI. (D) Sensitivity of M. abscessus eis2 KO strain to hydrogen peroxide (H2O2). Sensitivity to H2O2 was assessed by incubated bacterial cultures with H2O2 20 μM during 8 h. The amount of survival cells was determined by performing CFU tests at several hours post-infection (2, 4, 8 hpi). (E) Control of phagosomal rupture by M. abscessus Eis2. Phagosomal rupture was assessed by performing a FRET analysis as previously described [73]. Results are depicted as signal overlays per group with 1,000,000 events per condition acquired in not infected cells (NI cells), Heat killed M. abscessus (HK), wild-type M. abscessus (Mabs wt), KO strains (Δeis2MAB), KO strains complemented with eis2MAB (C.eis2MAB). All experiments were repeated twice or more in triplicates. Statistical analyses were performed with GraphPad PRISM6. Histograms with error bars represent means ± SD. Differences between means were analyzed by ANOVA and the Tukey post-test allowing multiple comparisons to be performed. ns = non-significant. * p<0.05, ** p<0.01, *** p<0.001, **** p<0.0001.