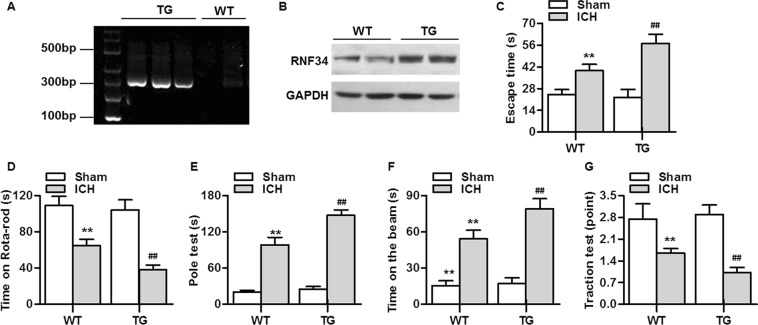
Figure 1.
RNF34 upregulation in mice exacerbates intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH)-induced neurological deficits. (A) The genotypes of wild-type (WT) and RNF34 transgenic (TG) mice were determined by PCR analysis of DNA isolated from tail biopsies. (B) Western blotting of RNF34 expression in brain tissues of WT and TG mice. (C–G) ICH model was established as described in Method section. Summarized data of neurological deficits as assessed by Morris water maze test (C), rotarod test (D), pole test (E), beam-crossing task (F), and traction test (G). **P < 0.01 vs. WT sham; ##P < 0.01 vs. WT ICH, n = 20/group.