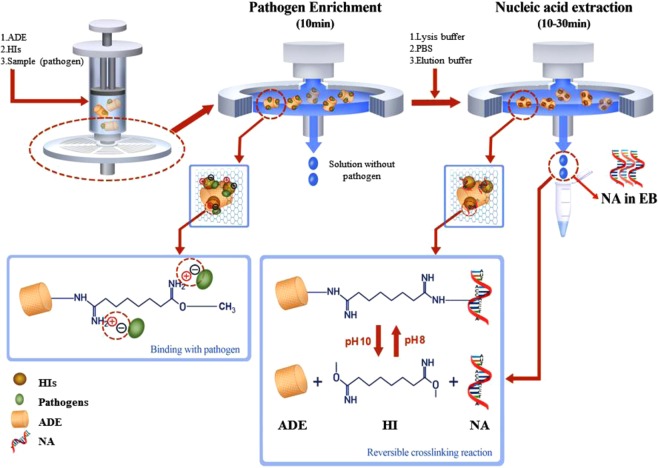
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram illustrating nucleic acid (NA) isolation using the hand-held syringe filter method based on amine-functionalized diatomaceous earth (ADE) in conjunction of homobifunctional imidoesters (HIs; DMA, DMS, DMP). Pathogen enrichment (top middle) and NA extraction (top right) can be completed with this hand-held system without the use of any chaotropic agents or instruments within as little as 20 min for 1 mL samples and 40 min for 50 mL samples. Shown by the dashed line from the pathogen enrichment process, the pathogens are absorbed onto the surface of the ADE; this is assisted by DMS via its positively charged amidine bonds, which can interact electrostatically with negatively charged pathogens (bottom left). The principle of NA isolation is shown by the dashed lines from the NA extraction process: DMS crosslinks the pathogen NA to ADE via a covalent bond in the reaction buffer (at pH 8); this can be broken by injecting a high-pH elution buffer (pH 10) into the filter, allowing the NA to be collected (bottom right).