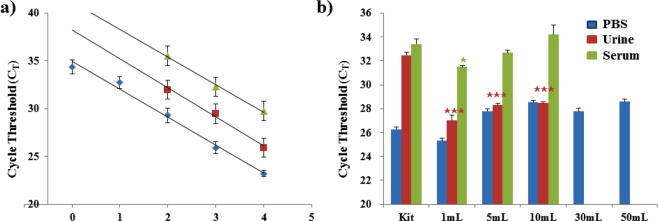
Figure 3.
Evaluation of the ADE-tube system for RNA isolation performance based on the cycle threshold (CT) values of real-time quantitative PCR (qPCR). (a) qPCR performance of isolated RNA templates from a dilution series of pathogen samples using commercial kits (Qiagen Kit (red) and Pathogen-specific Kit (green)) and the tube-based ADE–DMS system (ADE-Tube, blue). Brucella ovis in PBS was used as the pathogen. (b) Evaluation of the ADE-Tube system for large sample volumes in various sample matrices. The total amount of pathogenic bacteria was controlled to the same level for all of the parallel experiments. Here, 1 mL samples of 103 CFU/mL Brucella ovis were used. The kit used 200 μL of the 1 mL samples of 103 CFU/mL Brucella ovis in PBS, urine, and serum. To evaluate the capture performance of the assay for large-volume samples, the 1 mL samples were diluted serially to volumes up to 50 mL, using matched original solutions; the urine and serum samples were tested up to 10 mL. The tube-based assay used the entire 1 mL to 50 mL samples (103 CFU of Brucella ovis in PBS, urine, and serum) because of its different capacity. No CT values were obtained from the amplification of no-template controls (NTC) in any of these experiments. Error bars indicate standard deviation from the mean based on at least three independent experiments. The p-values were evaluated by Student’s t-test (★p < 0.05, ★★p < 0.01, ★★★p < 0.001; different colors indicate the matched samples compared with the kit).