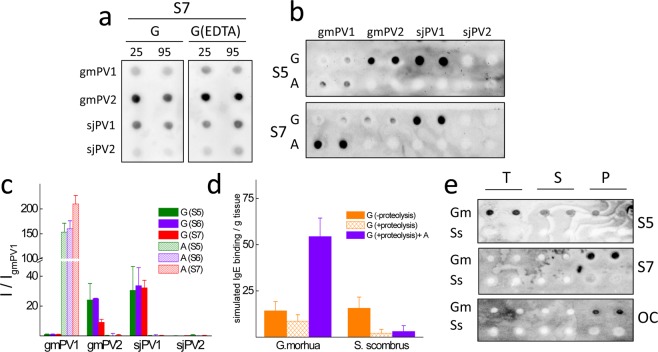
Figure 7.
Comparative serum IgE interaction of β-PV isoform folds. (a) Typical dot blots of the effect of temperature treatment of β-PV on the recognition by the IgE present in sera from fish-allergic patients. Key: G, Ca2+-bound globular monomer; G(EDTA), Ca2+-bound globular monomer treated with 5 mM EDTA; 25 and 95 °C, temperatures at which samples were kept for 15 min. (b) Typical dot blots of the effect of the β-PV isoform fold on the recognition by the IgE present in sera from fish-allergic patients. Key: G, Ca2+-bound globular monomer; A, amyloid aggregate; Si, sera from distinct fish-allergic patients. (c) IgE binding intensity obtained for the different conformations of β-PV isoforms compared to that of the Ca2+-bound globular fold of gmPV1 for distinct sera. (d) Simulation of fish muscle IgE binding from the content and properties of component β-PV isoforms. Key: G (−proteolysis), globular folds under proteolysis inhibition; G (+proteolysis), globular folds with proteolysis; G (+proteolysis)+A, globular folds with proteolysis and amyloids. (e) Serum IgE and OC immunoreactivities of Gadus morhua (Gm) and Scomber scombrus (Ss) muscle extracts (T) and their supernatant (S) and pellet (P) fractions. Blots were performed in duplicate using duplicated dots. All blots were loaded with 100 ng of protein per dot. The original membranes used in a, b and e panels are displayed in supplementary Fig. 7S.