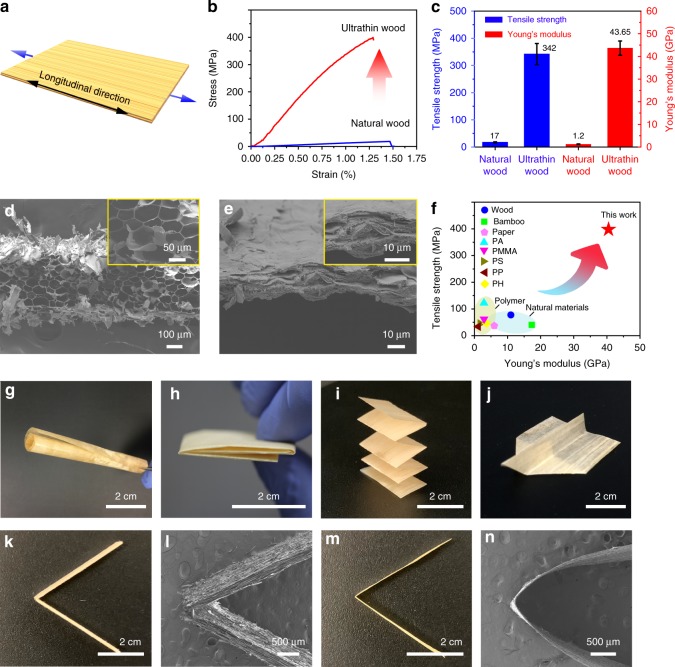
Fig. 3.
Mechanical properties of wood films. a Schematic of the tensile test along the longitudinal direction. b Corresponding tensile stress as a function of strain for the natural wood (blue line) and ultrathin wood film (red line). c Comparison of the tensile strength and Young’s modulus of the natural wood and ultrathin wood film. Error bars represent standard deviation. d, e SEM images of the tensile fracture surface of the natural wood and ultrathin wood film. f Comparison of the tensile strength and Young’s modulus of the ultrathin wood film with other widely used polymer and natural materials50. (PA: Polyamide; PMMA: Poly (methyl methacrylate); PS: Polystyrene; PP: Polypropylene) g–j Photographs of the ultrathin wood film demonstrating its flexibility and various origami designs. k, l Photograph and SEM image of the natural wood after bending, showing its rigid wood structure. m, n Photograph and SEM image of the ultrathin wood film after bending, showing its excellent flexibility and folding performance