Fig. 1.
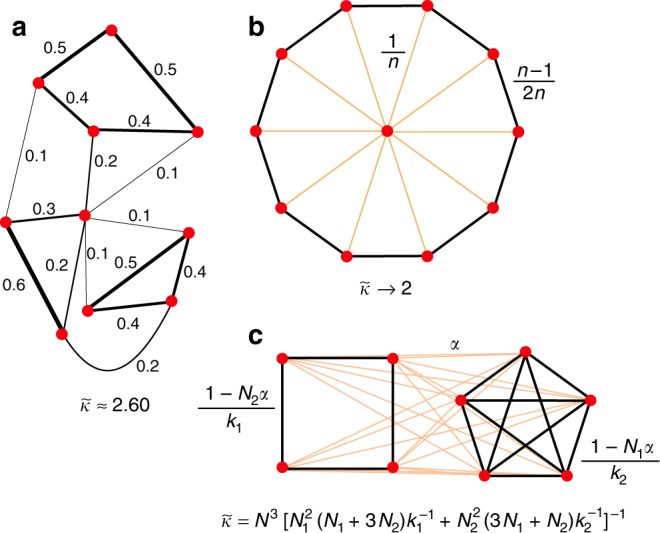
Isothermal graphs and their effective degrees. A graph is isothermal if the sum of edge weights is the same for each vertex. The effective degree of the graph, defined in Eq. (3), determines the outcome of evolutionary game dynamics. a An asymmetric isothermal graph; weights are shown for each edge. b A wheel graph, with one hub and wheel vertices. All connections with the hub have weight . All connections in the periphery have weight . As , the effective degree approaches 2. A formula for arbitrary is derived in Supplementary Note 3. c A 30-vertex graph generated with preferential attachment62 and linking number . Isothermal edge weights are obtained by quadratic programming (see Methods). The effective degree, , is less than the average topological degree, . d An island model, with edges of weight between each inter-island pair of vertices. Shown here are two islands: a -regular graph of size , and a -regular graph of size
