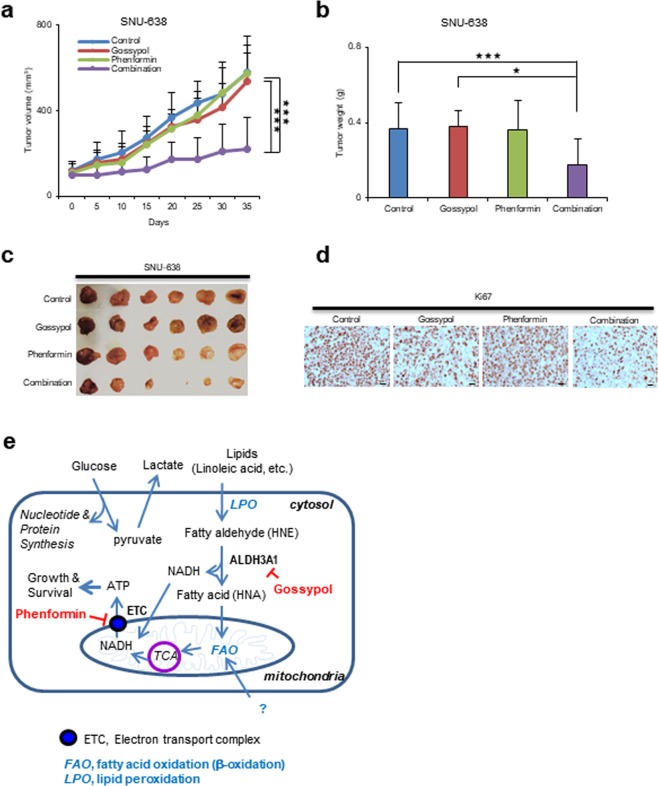
Figure 6.
Combined treatment with gossypol plus phenformin led to synergistic suppression of tumor growth in a mouse model of human gastric cancer. (a) SNU-638 (1.5 × 107) cells were injected into BALB/c nude mice (6–8 weeks old). When the volume of the tumor mass reached 110 mm3, mice were assigned randomly to one of four treatment groups (n = 6 per group): vehicle control, gossypol, phenformin, and gossypol plus phenformin. Gossypol (80 mg/kg body weight), phenformin (100 mg/kg body weight), and vehicle were administered orally 6 days/week. The graph shows a synergistic reduction in tumor growth after combined treatment with gossypol and phenformin. (b) The final weight of subcutaneous tumors derived from SNU-638 cells. (c) Representative photograph of subcutaneous tumors derived from SNU-638 cells. (d) IHC analysis of Ki67 staining in SNU-638 tumor xenograft tissues. Scale bar IH20 µm. (e) A proposed model for the synergistic mechanism underlying inhibition of ALDH3A1 and mitochondria complex 1 in gastric cancer. *p <0.05, **p <0.01, ***p <0.001.