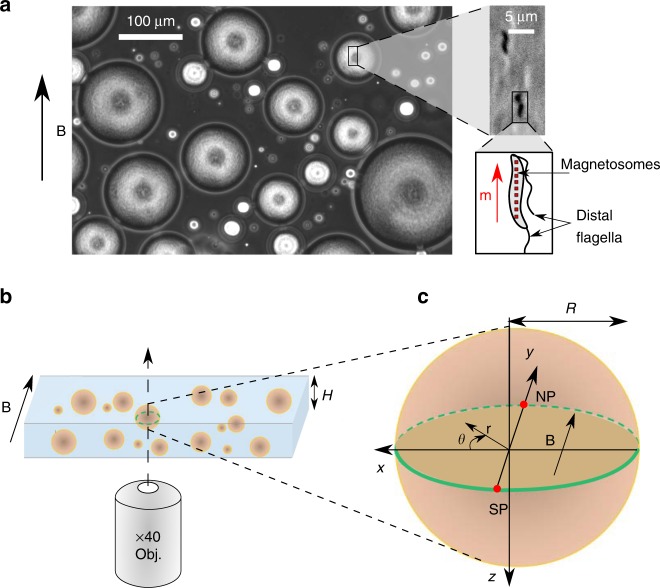
Fig. 1.
Water-in-oil emulsion of magnetotactic bacteria. a A phase-contrast image of an emulsion of magnetotactic bacteria (bacteria remain inside droplets) in hexadecane oil. A magnetic field of 4 mT is applied as indicated by the arrow (see the corresponding Supplementary Movie 1). A broad distribution of droplets radii is obtained, spanning typically from 20 to 120 µm. Zoom in: phase-contrast image of two magnetotactic bacteria Magnetospirillum gryphiswaldense MSR-1 (darkest zones) swimming along the magnetic field direction. Zoom in: Sketch of a magnetotactic bacterium carrying magnetosomes (red squares) and two distal flagella. The magnetosomes are aligned along the body, generating a magnetic moment . b Setup principle: a droplet, lying on the bottom plate of a pool of height 270 µm and placed on the stage of an inverted microscope, is observed at its equatorial plane with a objective. A uniform magnetic field is applied in the observation plane, parallel to the bottom and top plates of the pool. c Definitions of the north pole (NP), the south pole (SP) of the droplet and the spatial coordinates. is the droplet radius