Figure 2.
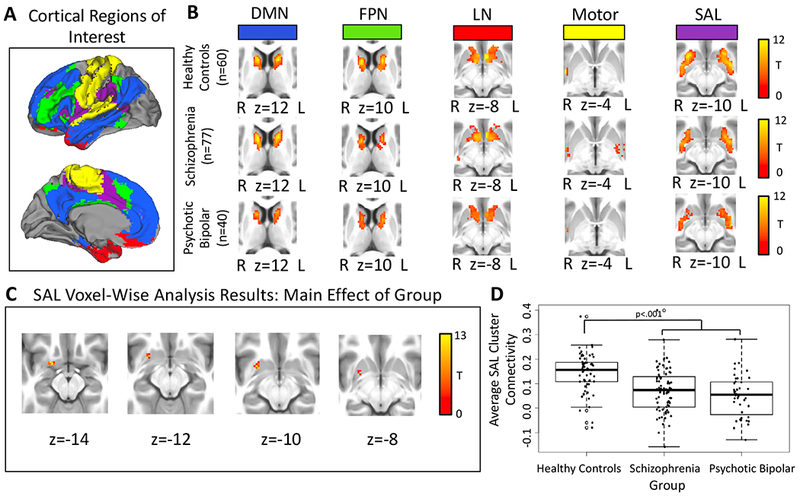
Panel A: Cortical parcellation used to define the five cortical regions-of-interest (ROIs). Panel B: The pattern of functional connectivity within the striatum for each cortical ROI in healthy controls, schizophrenia, and psychotic bipolar disorder. Results were thresholded at cluster-level Family-wise error-corrected p(FWE)=.05 for voxel-wise p(uncorrected)=.001. Panel C: Voxel-wise results for the salience network (SAL) cortical seed within the striatum revealed a main effect of group for the SAL cortical seed within the striatum, thresholded at whole-brain voxel-wise p(uncorrected)=.001. Panel D: Direct comparison between groups revealed decreased SAL network connectivity in the striatum in schizophrenia and psychotic bipolar disorder.
