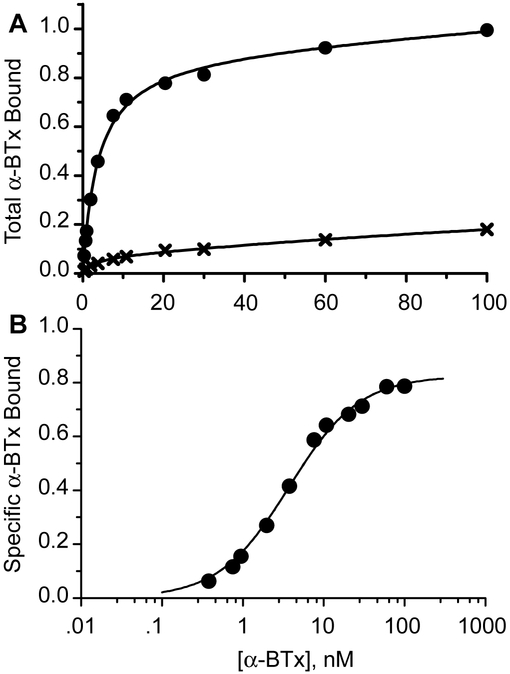
Fig. 4.
Concentration dependence of α-BTX binding to cell surface α4β2 AChRs containing the quintuple mutant α4 subunit. Panel A shows binding in the presence of 125I-α-BTX alone (filled circles) and in the presence of 2 mM nicotine (crosses); binding to cells transfected with the β2 subunit alone is subtracted. Total binding is expressed relative to that determined in the presence of 100 nM 125I-α-BTX. Smooth curves are fits to an equation for two binding sites in which the fraction of each site is variable. Panel B shows specific binding determined as the difference between total 125I-α-BTX binding and that in the presence of nicotine. The smooth curve is the result of fitting an equation for binding to a single class of sites to the data, yielding an apparent dissociation constant of 3.7 nM (Table 1).