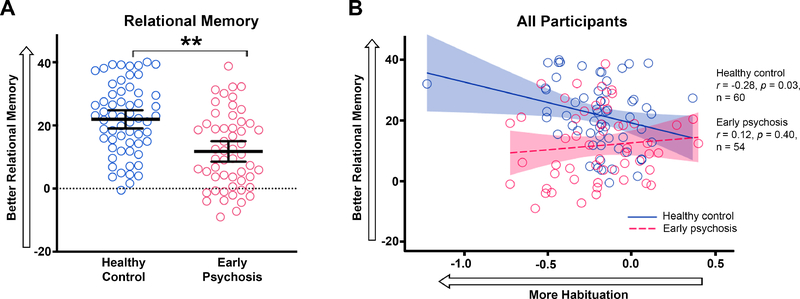
Figure 3.
Relational memory and habituation in the anterior hippocampus. A. The slope of preferential viewing of the correct face-scene pairing is shown for patients with early psychosis(red) and healthy control subjects (blue). Black bars indicate mean relational memory slope ± 95% confidence interval. Faster preferential viewing (positive slopes) indicate better relational memory. Patients with early psychosis had worse relational memory for trained face-scene pairs compared to healthy control subjects. B. In healthy control subjects, greater habituation in the anterior hippocampus was correlated with better relational memory performance. There was no relationship between habituation and relational memory in early psychosis patients. Asterisks indicate between-group comparisons significance for habituation slopes. * p ≤ 0.01.