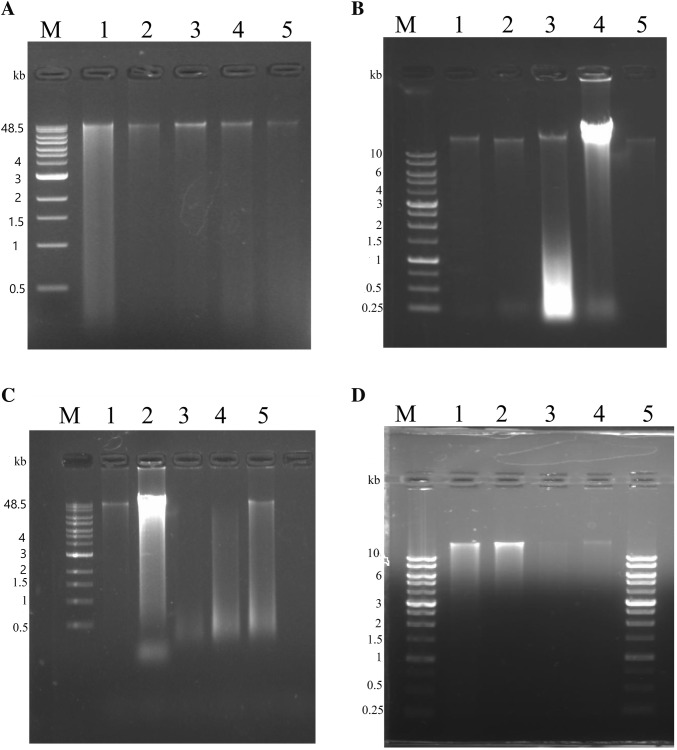
Fig. 1.
Gel electrophoresis of metagenomic DNA isolated from stool, fish gut, soil and milk samples. Metagenomic DNA was electrophoresed on a 0.8% agarose gel, stained with ethidium bromide and photographed in a gel documentation system. a Metagenomic DNA isolation by method A. Lane M: Quick-Load® 1 kb Extend DNA Ladder; lane 1: DNA isolated from stool sample; lane 2: DNA isolated from soil sample; lane 3: DNA isolated from fish gut (silver carp); lane 4: DNA isolated from fish gut (T. putitora); lane 5: DNA isolated from healthy mother’s milk. b Metagenomic DNA isolation by method B. Lane M: 1 Kb DNA Ladder RTU (GenedireX); lane 1: DNA isolated from fish gut (silver carp); lane 2: DNA isolated from fish gut (T. putitora); lane 3: DNA isolated from healthy mother’s milk; lane 4: DNA isolated from soil sample; lane 5: DNA isolated from stool sample. c Metagenomic DNA isolation by method C. Lane M: Quick-Load® 1 kb Extend DNA Ladder; lane 1: DNA isolated from soil; lane 2: DNA isolated from stool; lane 3: DNA isolated from fish gut (silver carp); lane 4: DNA isolated from fish gut (T. putitora); lane 5: DNA isolated from healthy mother’s milk. d Metagenomic DNA isolated from healthy mother’s milk. Lane M and lane 5: 1 kb DNA Ladder RTU (GenedireX); lane 1: DNA isolated from method A; lane 2: DNA isolated from modified method B; lane 3–4: DNA isolated from modified method C